AAP highlights pediatricians’ play role in improving oral health
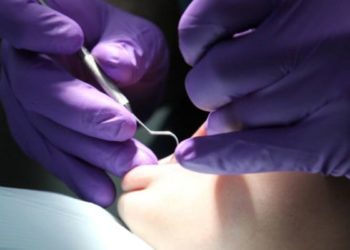
1. As the incidence of dental caries in young children has increased significantly in recent years and pediatricians often see young children more frequently than dentists, it is recognized that physicians can play an important role in preventing dental caries. The AAP recommends administering oral health risk assessments, counseling patients and families on the importance of reducing sugar intake and proper brush hygiene, and recommending that all children establish a dental home by 1 year of age.
Statement Rundown: Dental caries, including untreated dental caries, filled teeth, or teeth missing as a result of dental caries, has significantly increased in children aged 2 to 4 years from 19% to 24% between 1988-1994 and 1999-2004. During this same time period, dental caries has either decreased or stayed the same in older age groups. In this AAP Policy Statement, the role of pediatricians in helping improve and maintain childhood oral health is discussed. Pediatricians see younger children more frequently than dentists, and can play a vital role in improving oral health and preventing dental caries in these young children. Important risk factors in the development of dental caries include sugar consumption, early acquisition of Streptococcus mutans (bacteria most commonly associated with dental caries), and previous caries experience. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that pediatricians utilize a caries risk assessment, such as the AAP/Bright Futures Oral Health Risk Assessment Tool, to identify a child’s risk of caries. Anticipatory guidance for oral health should include reducing frequency and duration of sugar exposure, brushing children’s teeth as soon as first teeth erupt with frequent parental monitoring until 8 years of age, proper fluoride use based on previous AAP recommendations, and recommending that all children establish a dental home by 1 year of age. Physicians aware of these recommendations may help identify and prevent dental caries in children at an earlier age and improve overall oral health of their patients.
Click to read the policy statement published today in Pediatrics
Relevant Reading: Fluoride varnish efficacy in preventing early childhood caries
More from this author: Standardized central line care practices reduce bloodstream infections; Maternal verbal interaction more common than paternal during infancy; Socioeconomic status linked to specific infant dietary patterns; Off-hours PICU admissions not linked to increased mortality; Pediatric renal and thyroid cancer rates increase
Image: PD
©2014 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.