Diabetes linked to increased mortality in China
1. In a 7-year nationwide prospective study of over a half-million Chinese adults, diabetes was more common in urban than rural areas.
2. Diabetes was linked to increased mortality due to ischemic heart disease, stroke, chronic liver disease, and infections.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
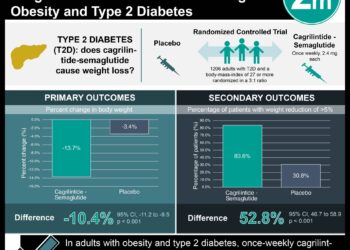
Study Rundown: Diabetes remains one of the most common chronic medical conditions in the United States. In China, the prevalence of diabetes has more than quadrupled in recent decades. The impact of diabetes on morbidity and mortality in China is unknown, and the authors of this study sought out to perform a nationwide prospective study to determine the association between diabetes and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban areas in China. Among more than 500,000 people who responded to study questionnaires, 5.9% of people had diabetes. Individuals with diabetes had twice the risk of all-cause mortality compared to individuals without diabetes. Furthermore, this risk was increased for people in rural areas than those in urban areas. People with diabetes also had at least twice the increased risk of mortality due to ischemic heart disease, stroke, chronic liver disease, and infections.
Overall, this study suggests that diabetes is associated with increased overall mortality and specifically with mortality due to a number of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular diseases. A major limitation of this study is that diabetes prevalence was estimated using random plasma glucose and fasting plasma glucose, not hemoglobin A1c or 2-hour glucose measurements. Additionally the prevalence of type I diabetes in this population was unknown which may serve to confound the results.
Click to read the study in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Diabetes and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort of one million U.S. adults
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This study utilized the China Kadoorie Biobank, which consisted of baseline surveys from 2004-2008 across 10 localities in urban and rural China. Participants included 512,869 residents aged 35-74 years for whom health histories and labs were obtained. These people were followed up until 2014. At baseline, 5.9% of people had diabetes, of which 2.8% was detected by screening. Diabetics were more likely to be less physically active and have higher body mass index, blood pressure, and history of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease. The prevalence of diabetes was higher in urban areas at 8.1% compared to rural areas at 4.1%. With 3.64 million person-years of follow-up, a total of 24,909 people died, 3,384 of whom had been diagnosed with diabetes. People with diabetes had twice the increased risk of all-cause mortality compared to individuals without diabetes (1,373 vs 646 deaths per 100,000; RR 2.00 [CI95% 1.93-2.08]). Interestingly, this risk was greater in rural areas (RR 2.17 [CI95% 2.07-2.29]) than in urban areas (RR 1.83 [CI95% 1.73-1.94]). Furthermore, diabetes was associated with increased mortality due to a number of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular diseases- specifically, ischemic heart disease (RR 2.40 [CI95% 2.19-2.63]), stroke (RR 1.98 [CI95% 1.81-2.17]), chronic liver disease (RR 2.32 [CI95% 1.76-3.06]), and infections (RR 2.29 [CI95% 1.76-2.99]).
Image: PD
©2017 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.