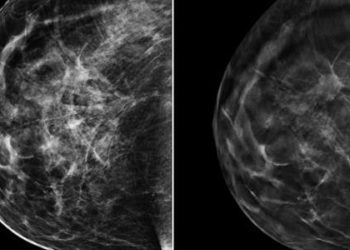
First-degree family history of breast cancer associated with increased risk of breast cancer in older women
1. In this prospective cohort study, first-degree family history of breast cancer was associated with increased risk of breast cancer in women 65 years and older.
2. In women 65 to 74 years old, the risk was highest in those with fatty breasts whereas in women 75 years and older the risk was highest among those with dense breasts.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: While family history of a first-degree relative with breast cancer is a strong risk factor for breast cancer in younger women, it is unclear how influential this risk factor is for older women. This prospective cohort study aimed to determine whether first-degree family history is associated with increased risk of breast cancer among older women and to identify whether this association varies by breast density.
First-degree family history was associated with statistically significant increased risk of breast cancer in women 65 years and older. It did not matter whether the first-degree relative with breast cancer was younger or older than 50. For women 65 to 74 years old, risk associated with first-degree relative was highest in those with fatty breasts and in women 75 years and older the risk was highest among those with dense breasts. Strengths of this study included use of a large population-based sample with diverse socioeconomic and ethnic backgrounds. However, limitations included use of only first-degree relative information, as there is evidence that second-degree relatives with breast cancer may also confer increased risk.
Click to read the study, published in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Family History, Mammographic Density, and Risk of Breast Cancer
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This prospective cohort study was conducted between 1996 and 2012 using seven breast cancer registries from seven sites across the USA. These registries included women who presented for screening mammographies. The study’s sample consisted of 472,220 mammograms from 403,268 women 65 years and older who provided self-reported information about first-degree relative family history between 1996 and 2012. Women with a diagnosis of breast cancer prior to or within 3 months of eligible mammogram, or those with breast implants, mastectomy or without BI-RADS breast density were excluded. The exposure of interest was first-degree family of breast cancer and they were followed for a mean (SD) of 6.3 (3.2) years for the outcome of incident breast cancer. The 5-year cumulative incidence of invasive breast cancer by first-degree family history, breast density, and age groups were estimated. Cox proportional hazards models were fit to estimate the association of first-degree family history with risk of invasive breast cancer.
In the sample, first-degree family history was associated with an increased risk of breast cancer among women aged 65 and older: 65-74 years HR 1.48; 95% CI 1.35-1.61, 75 years and older HR 1.44; 95% CI 1.28-1.62. The age of the first degree relative upon diagnosis of breast cancer did not statistically alter risk of breast cancer in these women. However, among women 65 to 74 years old, the risk associated with first-degree relative family history was highest among women with fatty breasts (HR 1.67; 95% CI 1.27-2.21) whereas in women who were 75 years and older, the risk associated with first-degree relative family history was highest among those with dense breasts (HR 1.55; 95% CI 1.29-1.87).
Image: PD
©2018 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.