Nivolumab/Ipilimumab vs Nivolumab Alone in Advanced Cancers Other Than Melanoma
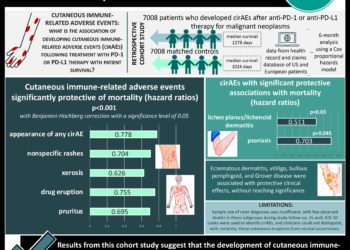
1. Pooled overall survival and progression-free survival HR were found to be 0.95 and 0.88 for nivolumab/ipilimumab vs. nivolumab.
2. Pooled OR for grade 3-4 adverse events was found to be 1.84 for the combination compared to monotherapy
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Nivolumab/ipilimumab combination therapy has demonstrated improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) vs. nivolumab alone in metastatic melanoma. However, this comparison has not been well established in other forms of advanced cancers, and limited direct comparisons exist. This study was a meta-analysis that assessed the efficacy and safety of nivolumab/ipilimumab vs. nivolumab alone in advanced cancers beyond melanoma. Primary outcomes investigated were OS, PFS, grade 3 or 4 adverse events (AEs), and treatment-related discontinuations. Eight studies with a total of 1727 patients with a variety of cancers (lung cancer, pleural mesothelioma, urothelial carcinoma, esophagogastric carcinoma, sarcoma, and glioblastoma multiforme) were included in the meta-analysis. With regards to OS, it was found that nivolumab/ipilimumab had a pooled HR 0.95 with 4 studies showing lower median OS compared to nivolumab monotherapy. With regards to PFS, nivolumab/ipilimumab had a pooled HR 0.88 compared to nivolumab monotherapy, with a single large study (40% weight) accounting for this marginal improvement (HR 0.84 in that study). With regards to safety, the pooled OR of grade 3 to 4 AEs for nivolumab/ipilimumab vs. nivolumab alone was 1.84, and treatment-related discontinuations with nivolumab/ipilimumab vs. nivolumab alone had a pooled OR of 1.96. The most common grade 3 to 4 AEs in the combination group included hepatotoxicity (9.7%), gastrointestinal toxicity (4.0%), pneumonitis (3.6%), endocrine dysfunction (3.4%), dermatitis (3.2%), and fatigue (3.2%), all of which had lower incidence rates in the monotherapy group. The strengths of this study included its homogeneity and the limitations of this study included the low number of included studies and the exclusion of certain dosing regimens. Overall, this study found that combination therapy with nivolumab/ipilimumab has similar efficacy and higher toxicity compared to nivolumab monotherapy in many advanced cancers other than melanoma.
Click to read the study in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma
In-Depth [ meta-analysis]: This meta-analysis searched through PubMed, EBSCO Information Services, Embase, and Cochrane Library for studies of nivolumab/ipilimumab vs. nivolumab alone for the treatment of advanced cancers other than melanoma published from database inception to October 31, 2022. Eligibility criteria included only prospective studies and certain standard dosing for nivolumab/ipilimumab and nivolumab. The initial search identified 168 publications and 8 studies (1727 patients, nivolumab/ipilimumab 854, nivolumab 873) were included in the data analysis. These studies included lung cancer, pleural mesothelioma, urothelial carcinoma, esophagogastric carcinoma, sarcoma, and glioblastoma multiforme. With regards to OS, it was found that nivolumab/ipilimumab had a pooled HR of 0.95 (95%CI, 0.85-1.06; p=.36; I2 = 0%), with 4 studies showing lower median OS compared to nivolumab monotherapy. With regards to PFS, nivolumab/ipilimumab had a pooled HR 0.88 (95%CI, 0.79-0.98; p=.02; I2 = 0%) compared to nivolumab monotherapy, with the largest study accounting for this marginal improvement (HR 0.84 in that study). With regards to safety, the OR of grade 3 to 4 AEs for nivolumab/ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone was 1.84 (95%CI, 1.47-2.31; p<.001; I2 = 0%), and treatment-related discontinuations with nivolumab/ipilimumab vs nivolumab alone had an OR of 1.96 (95%CI, 1.45-2.66; p<.001; I2 = 2%). The most common grade 3 to 4 AEs in the combination group included hepatotoxicity (9.7%), gastrointestinal toxicity (4.0%), pneumonitis (3.6%), endocrine dysfunction (3.4%), dermatitis (3.2%), and fatigue (3.2%), all of which had lower incidence rates in the monotherapy group. Overall, this study found that combination therapy with nivolumab/ipilimumab has similar efficacy and higher toxicity compared to nivolumab monotherapy in many advanced cancers other than melanoma.
Image: PD
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.