Subcutaneous amivantamab with lazertinib is non-inferior to intravenous administration, with fewer adverse reactions
1. Subcutaneous amivantamab combined with lazertinib was non-inferior to intravenous amivantamab with lazertinib in terms of efficacy in treating refractory EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
2. Subcutaneous amivantamab resulted in fewer infusion-related reactions, allowed for shorter administration times, and increased patient convenience compared to the intravenous formulation
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The present study is a randomized controlled trial that assessed the efficacy of subcutaneous amivantamab with lazertinib compared to intravenous amivantamab with lazertinib. It included patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who had progressed following treatment with osimertinib and platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized to receive either subcutaneous or intravenous amivantamab. The study demonstrated that subcutaneous amivantamab, combined with lazertinib, was non-inferior to its intravenous counterpart in terms of pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Additionally, the subcutaneous formulation resulted in fewer infusion-related reactions and venous thromboembolic events. Strengths of this study include its randomized controlled design, large sample size, and comprehensive assessment of pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety. Limitations include a short follow-up period of seven months, which may limit the assessment of long-term safety and efficacy. Overall, the study supports the use of subcutaneous amivantamab over the intravenous formulation for patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC.
Click to read the study in The Journal of Clinical Oncology
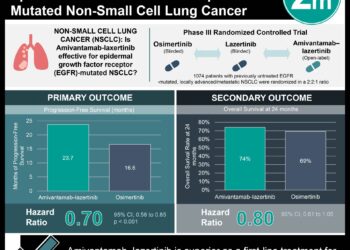
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study assessed the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous versus intravenous amivantamab, both combined with lazertinib, in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC who progressed after osimertinib and platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either subcutaneous or intravenous amivantamab. The primary endpoints were pharmacokinetic noninferiority, measured by trough concentrations (Ctrough) and area under the curve (AUCD1-D15). Secondary endpoints included objective response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). 418 patients were included in the trial. Subcutaneous amivantamab showed comparable pharmacokinetics to the intravenous form, with geometric mean ratios of Ctrough at cycle-2-day-1 of 1.15 (90% CI, 1.04-1.26) and at cycle-4-day-1 of 1.42 (90% CI, 1.27-1.61), and cycle-2 AUCD1-D15 of 1.03 (90% CI, 0.98-1.09). Median PFS was 6.1 months for subcutaneous and 4.3 months for intravenous (HR for disease progression or death, 0.84; 95% CI, 0.64-1.10; P=0.20). Furthermore, OS was significantly longer for subcutaneous (HR for death, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.42-0.92; nominal P=0.02). Importantly, fewer infusion-related reactions were observed in the subcutaneous group (13% vs. 66%). Overall, this study supports the use of subcutaneous amivantamab over the intravenous formulation in terms of efficacy and safety for the treatment of NSCLC.
Image: PD
©2024 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.