#VisualAbstract: Ianalumab shows a dose-related improvement in disease activity in Sjögren’s syndrome without serious adverse events
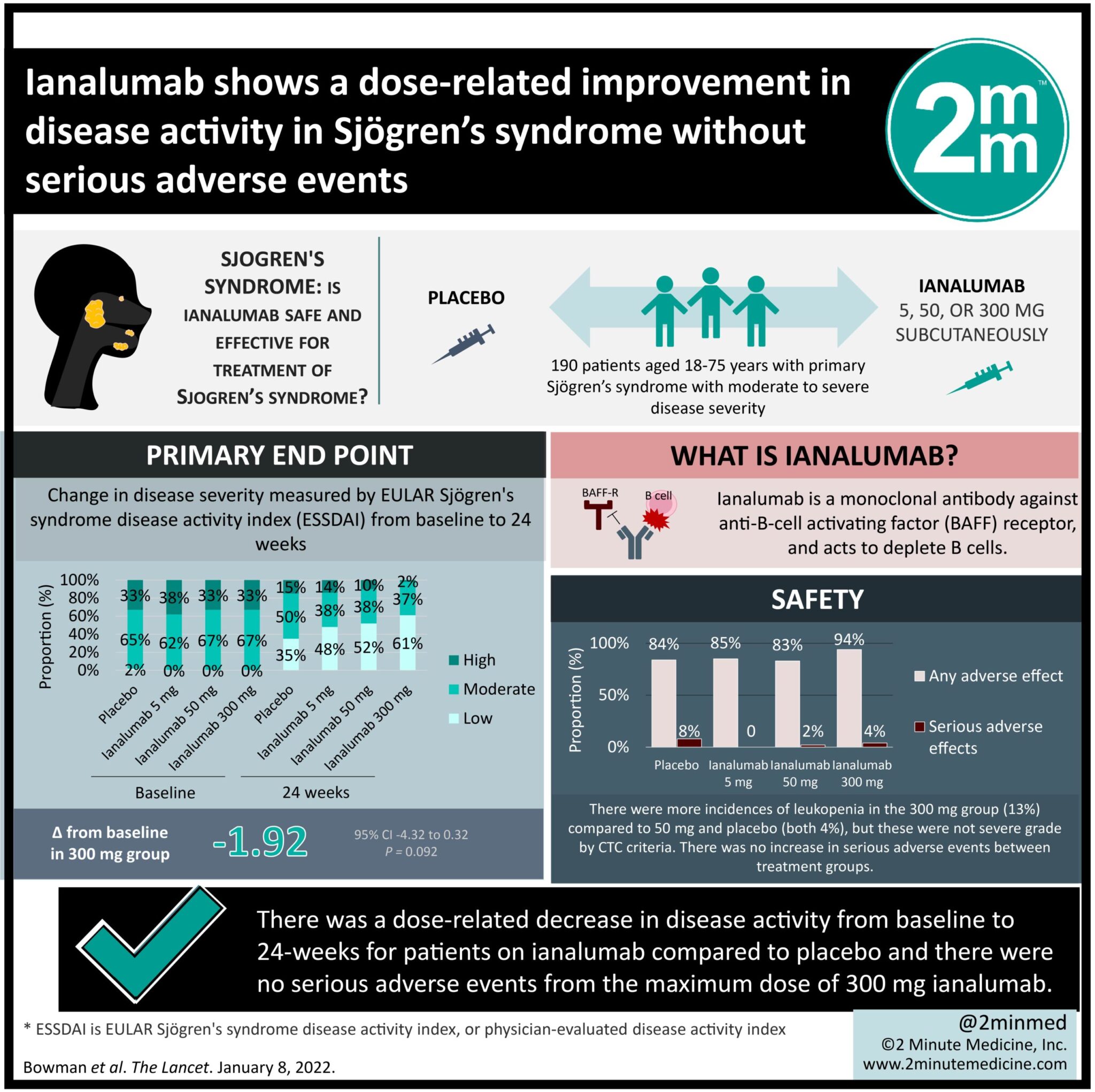
1. There was a dose-related decrease in disease activity from baseline to 24-weeks for patients on ianalumab compared to placebo.
2. There were no serious adverse events from the maximum dose of 300 mg ianalumab, and it was well tolerated by trial participants.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder which is currently only treated with symptomatic management of common features, such as dryness, fatigue, and pain. The goal of this phase 2 randomized control trial was to evaluate the safe and effective doses of a new biologic, ianalumab. Patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome were enrolled and randomized (1:1:1:1) to receive either subcutaneous placebo, 5 mg ianalumab, 50 mg ianalumab, or 300 mg ianalumab over a 24-week period. The primary outcome was a physician-evaluated disease activity index (ESSDAI) score measured every 4 weeks from baseline. Other scores measured included the EULAR Sjögren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) and Patient Global Assessment (PaGA). Measurements of salivary and tear production were also measured throughout the study period. This study met its primary outcome of showing a dose-dependent decrease in ESSDAI score during the 24-week treatment period, with the greatest differences seen in the 300 mg ianalumab group. Adverse events on the maximum dose of ianalumab were also found to be minimal, with the main reported adverse being a local site reaction to the injection. Limitations to this study include a large placebo effect seen, which should be considered for future trials. Nonetheless, this study opens the possibility of future trials for the treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome.
Click to read the study in The Lancet.
Relevant Reading: Severe health-related quality of life impairment in active primary Sjögren’s syndrome and patient-reported outcomes: data from a large therapeutic trial.
In-Depth [randomized control trial]: Patients aged 18-75 years with primary Sjögren’s were eligible for this double-blind randomized control trial. Participants (n=190) were randomly assigned to receive either placebo (n=49) or 5 mg (n=47), 50 mg (n=47) or 300 mg (n=47) of ianalumab. Most patients were female (95%), and average age was approximately 50 years. The primary outcome was reported as disease activity using the ESSDAI score and the Physician Global Assessment (PhGA). Patient reported severity was collected using the PaGA and the ESSPRI score which measures the symptoms of pain, dryness and fatigue. Secondary outcomes included the objective measurements of tears and salivary flow, as well as other quality of life scales. Assessment was done every 4 weeks from baseline up to 24 weeks.
A dose-dependent decrease in ESSDAI score was seen over the 24-week period. Adjusted for the decrease also seen in the placebo group, the 300 mg ianalumab group saw a -1.92 point (95% CI -4.15 to 0.32, p=0.093) change in least-squares mean ESSDAI score from baseline. No major change was seen in ESSPRI. There was a decrease in PhGA by -8.4 (p=0.022) and PaGA by -4.77 (p=0.32). Tear flow did not change significantly, but stimulated salivary flow improved significantly with a least-squares mean change of 0.20 mL/min (p=0.037) among ianalumab 300 mg versus placebo. There were more incidences of leukopenia in the 300 mg group (13%) compared to 50 mg and placebo (both 4%), but these were not severe grade by CTC criteria. There was no increase in serious adverse events between treatment groups.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.

![No benefit with hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) over placebo in Sjogren’s Syndrome [JOQUER Trial]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Sjogren_syndrome_2-350x250.jpg)






