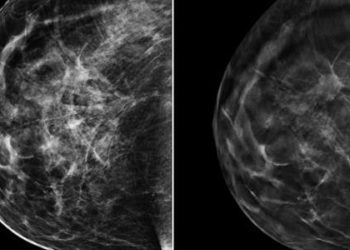
Breast ultrasound screening model reveals increased costs for small benefits
1. Microsimulation models demonstrated limited health benefits of supplemental ultrasonography for women with dense breasts and substantial increases in cost.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Increased breast density is a risk factor for breast cancer, but its integration into screening remains challenging. An increasing number of states are enacting laws requiring patient education about breast density and consideration of additional screening for women with dense breasts and a negative mammogram. One such supplement to screening is ultrasonography, which is a widely available and relatively low-cost adjunct screening modality. The current study evaluated the benefits, harms, and cost-effectiveness of supplemental screening ultrasonography for women with dense breasts. Using established breast cancer models, the addition of ultrasonography as a screening method resulted in only marginal improvements in preventing breast cancer deaths, with very high healthcare costs. Even considering annual or biennual mammograms, as well as extremely or heterogeneously dense breasts, ultrasonographic screening was highly cost-ineffective. A significant limitation to this model is the relative lack of evidence better establishing sensitivity and specificity of supplemental ultrasonography. Additionally, the cost of supplemental ultrasonography was estimated using related diagnostic costs since no reimbursement rates currently exist. However, overall, this model shows that supplemental ultrasonographic screening will likely not be a cost-effective measure.
Click to read the study today in the Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: American College of Radiology Statement on Reporting Breast Density in Mammography Reports and Patient Summaries
In-Depth [microsimulation model]: The study used 3 microsimulation models developed as part of the National Cancer Institute-funded Cancer Intervention and Surveillance modeling Network consortium. The authors identified a single American College of Radiology study of ultrasonography among women with at least 1 breast cancer risk factor to determine a screening ultrasound sensitivity of 55% and 94% specificity. Models assumed 100% adherence and included short-term reductions in quality of life (0.6% for 1 week per screening examination) or positive result (10.5% or 5 weeks). Using this model, the authors predicted that in a lifetime, supplemental ultrasonography would result in 504 exams per 1000 women aged 50-74 with biennial mammography, and 3827 per 1000 women aged 40-74 years and annual mammography. Compared with biennial mammography for women 50-74, supplemental ultrasonography for women with extremely dense breasts avoided 0.30 additional breast cancer deaths and produced 1.1 additional Quality Adjusted Life Years (QALYs) at a cost effectiveness ratio of $246,000/QALY per 1000 women. When expanded to heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts, the models predicted 0.36 additional deaths avoided, 1.7 additional QALYs gained, and a cost-effectiveness ratio of $325,000/QALY per 1000 women. When considering annual mammography for women age 40-74, supplemental ultrasonography for women with heterogeneously or extremely dense breasts resulted in 0.43 additional deaths avoided and 3.0 additional QALYs at a cost-effectiveness ratio of $728,000/QALY.
Image: CC/Wiki
©2014 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.