High body fat percentage and low BMI independently associated with increased mortality
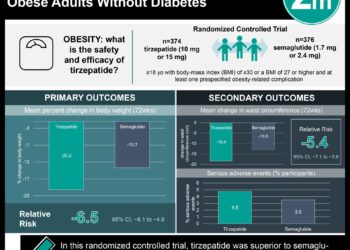
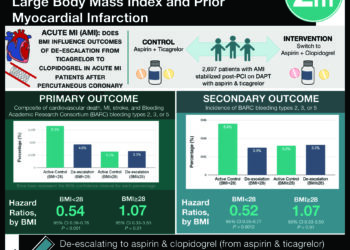
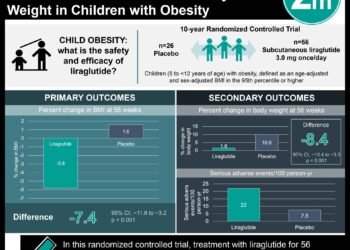
1. From a prospective cohort study, increasing body fat percentage and decreasing BMI were associated with reduced survival.
2. The results of this study suggest that BMI may be an inappropriate measurement of adiposity.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Many population cohort studies have reported that excess adiposity, typically assessed by BMI, is associated with an increased risk for all-cause death. However, recent studies also indicated that elevated BMI (25-29.9 kg/m2, overweight classification) is correlated with decreased mortality risk. In response to this contradiction, it has been suggested that BMI may be an imperfect measure of adiposity, as it does not directly measure body fat. The authors of this study, therefore, aimed to assess the relationship of BMI and body fat percentage with all-cause mortality. They observed that when BMI and body fat percentage were analyzed together, mortality rates increased as BMI decreased and body fat percentage increased. This study is strengthened due to its large cohort population; however, it may not be generalizable due to its lack of diversity among participant ethnicity (largely female and Caucasian). The results are also limited due to the lack of data on smoking and physical activity, which restricted the authors’ abilities to adjust for these factors. Overall, the study suggests that both decreased BMI and increased body fat are independently associated with higher mortality, providing further evidence that BMI may be an inappropriate measure of adiposity.
Click to read the study, published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Decreased muscle mass and increased central adiposity are independently related to mortality in older men
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: Mortality, BMI, and body fat percentage were assessed for 49,476 women and 4,944 men, aged 40 years or older, partaking in bone mineral density (BMD) testing in Manitoba. Participants were then followed from the initial date of the testing until death or end of the study. BMI and body fat percentage were analyzed both separately and together using fully adjusted models. Crude death rates decreased from 18.6 per 1000 person-years for the lowest BMI classification (≤22.85 kg/m2) to 13.9 per 1000 person-years for the highest BMI classification (>30.84 kg/m2) in women; similar trends were observed for men (p for trend <0.001, in both women and men). Furthermore, high body fat percentage was independently associated with significantly higher mortality in women (hazard ratio, 1.19 [95%CI, 1.08 to 1.32] in the highest body fat percentage category, >38.66%) and men (hazard ratio, 1.59 [95%CI, 1.28 to 1.96] in the highest body fat percentage category, >36.14%).
Image: PD
©2016 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.