Adjuvant gefitinib compared to chemotherapy after lung cancer resection did not improve survival
1. The median disease-free survival for gefitinib group and cisplatin/vinorelbine group was 35.9 and 25.1 months, respectively.
2. Patients receiving gefitinib experienced adverse events such as an increase in alanine transferase and aspartate aminotransferase, diarrhea and dermatitis acneiform.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
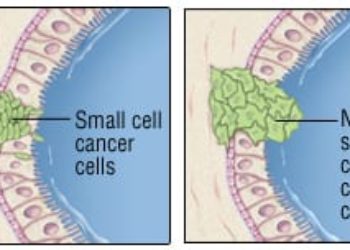
Study Rundown: For patients with completely resected stage II-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the standard of care is adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy. In recent years, studies have showed that platinum-doublet chemotherapy with cisplatin and vinorelbine modestly improve survival outcomes. For patients with metastatic NSCLC with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation, osimertinib, a third generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), is the standard of care as adjuvant treatment to the platinum-doublet chemotherapy. However, for patients who are not able to take or tolerate osimertinib, adjuvant gefitinib could be a potential alternative option. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gefitinib as an adjuvant treatment for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutation. Patients were divided into two groups: one receiving gefitinib and the other receiving cisplatin and vinorelbine for 2 years. The median disease-free survival (DFS) for gefitinib group and cisplatin/vinorelbine group was 35.9 and 25.1 months, respectively. The 5-year overall survival (OS) was 78.0% in the gefitinib group and 74.6% in the cisplatin/vinorelbine group. Commonly reported adverse events in patients receiving gefitinib included an increase in alanine transferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), diarrhea and dermatitis acneiform. Limitations to the study include having low number of patients in the study and the challenges in generalizing the findings to patients with different ethnicities. Overall, this study demonstrated that gefitinib does not show a significant difference in the DFS and OS between the gefitinib and the cisplatin/vinorelbine group and can be considered as an alternative if the patient is unable to tolerate chemotherapy though this trial was not designed for non-inferiority.
Click to read the study in Journal of Clinical Oncology
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This was an open-label, phase III, randomized trial of 234 patients at 25 institutes in Japan. Patients were eligible if they had stage II-III NSCLC and underwent complete surgical resections within 3-8 weeks. Their primary tumor had to have either exon 19 deletion (Del 19) or L858R mutation of the EGFR gene detected. Patients were assigned to receive gefitinib (250mg once daily) for 24 months or cisplatin (80mg/m2 on day 1) and vinorelbine (25 mg/m2 on days 1 and 8). The primary end point was the disease-free-survival (DFS), and it was measured through a blinded, independent review of the first relapse or second primary cancer detection. The median DFS for gefitinib group and cisplatin/vinorelbine group was 35.9 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 30.0-47.7) and 25.1 (95% CI: 17.7-41.8) months, respectively. The corresponding hazards ratio was 0.92 (95% CI: 0.67-1.28; P value= 0.63). There was no difference in the OS (hazards ratio [HR]: 1.03, 95% CI: 0.65-1.65). The 5-year OS was 78.0% in the gefitinib group and 74.6% in the cisplatin/vinorelbine group. There were no deaths and 77 patients in the gefitinib group experienced disease relapse compared to 65 patients in the cisplatin/vinorelbine group. Commonly reported adverse events in patients receiving gefitinib included increase in ALT (68.7%) and AST (65.2%), diarrhea (65.2%) and dermatitis acneiform (58.3%).
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.