Dacomitinib may be effective in EGFR-associated lung cancer
1. Patients with advanced EGFR-associated non-small-cell lung cancer treated with dacomitinib had increased progression-free survival as compared to those without mutations.
2. Common adverse side effects including diarrhea, dermatitis, dry skin, and stomatitis were comparable to those of first generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) of endothelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) have previously been shown to significantly increase progression-free survival in patients with EGFR-mutant, non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite this, no difference in overall survival has been demonstrated with EGFR inhibitors, in large part due to tumor cells’ ability to develop escape mutations that bypass EGFR. Dacomitinib is a second generation TKI which is both an irreversible inhibitor of EGFR and a pan-inhibitor of the accessory human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) pathway. The purpose of this trial was to evaluate the role of dacomitinib as first-line therapy in patients with EGFR-associated NSCLC.
In this phase II trial, 89 treatment-naïve NSCLC patients with either molecular or clinical characteristics associated with TKI response were given dacomitinib as first line therapy. The results demonstrated a significantly increased 4-month progression-free survival rate in the EGFR-mutant population versus the non-mutated cohort. Interestingly, the estimated median progression-free survival for the favorable EGFR mutated group was over 40 months, which was significantly longer than prior studies using afatinib, another second generation EGFR inhibitor that does not have HER activity. The safety of dacomitinib were comparable in both frequency and severity to adverse events of currently used first-generation EGFR inhibitors. The results of this trial support the use of dacomitinib as first-line therapy for EGFR-associated NSCLC. However, limitations of this study included its relatively short median follow up time of 24.8 months, small patient population, and lack of randomized comparisons to first-generation EGFR inhibitors.
Click to read the study in the Lancet Oncology
Relevant reading: Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer
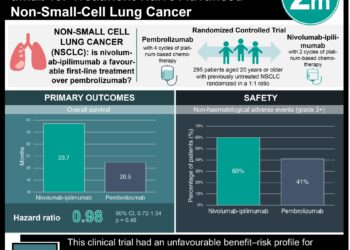
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: In this multicenter, open-label, phase II trial, 45 patients with favorable EGFR mutation status and 44 with unknown mutation status and clinical characteristics predicting response to TKI, were given dacomitinib as first-line therapy. Progression-free survival at 4 months was the primary endpoint. In patients with EGFR mutations, 95% met the 4 month criteria for progression-free survival (95% CI: 83.2-98.9%), while 68.2% of patients with unknown EGFR mutation status met the criteria (95% CI: 44.6-83.4%). In patients with known EGFR wild-type status, only 33.3% were progression free at 4 months (95% CI: 10.9-58.0%). This result corresponded to an estimated overall survival of 40.2 months (95% CI: 29.0-not reached), 24.3 months (95% CI: 19.0-35.1), and 19.7 months (95% CI: 3.5-24.3), respectively. The most common adverse events were diarrhea in 83 patients, dermatitis in 69 patients, dry skin in 39 patients, and stomatitis in 36 patients. The majority of these side effects were mild in nature. The null hypothesis of progression-free survival of 50% or less at 4 months was tested using the Kaplan-Meier method in a Fleming single-stage trial design.
More from this author: Erlotinib does not demonstrate increased survival in ovarian epithelial carcinomas, Afatinib shows increased progression-free survival in non-small-cell lung cancer, New method may predict response to chemotherapy for lung cancer, Escalated-dose radiotherapy did not increase survival in prostate cancer, Stereotactic radiosurgery promising for patients with multiple brain metastases
Image: CC/Yale Rosen
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.