Device closure for patent foramen ovale decreases recurrent stroke risk compared to medical therapy alone
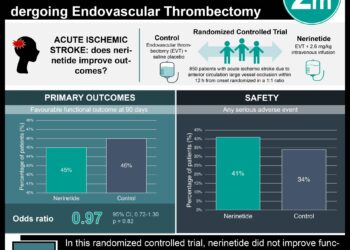
1. Transcatheter device closure for patent foramen ovale (PFO) decreased recurrent stroke risk compared to medical therapy alone.
2. However, PFO closure was also found to be associated with increased rates of atrial fibrillation (AF) compared to medical therapy alone.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Cryptogenic strokes have no identified cause and constitute about one third of ischemic strokes. Data suggests that PFO is linked to cryptogenic stroke. Therefore, transcatheter device closure of a PFO may decrease the chance of recurrent stroke. Although past studies have not shown that PFO closure was better than using medical therapy alone, there is now new data. This systemic review and meta-analysis provides an updated summary of studies evaluating transcatheter PFO closure versus medical therapy alone for recurrent stroke prevention in individuals with PFO and cryptogenic stroke. Using information from several databases, the authors found that transcatheter device closure for PFO decreases recurrent stroke risk compared to medical therapy alone. However, PFO closure was also found to be associated with increased rates of AF compared to medical therapy alone. Considering that recurrent stroke rates are small, the authors suggest that clinicians and patients should work together to make an educated decision about PFO closure.
A strength of the study is that it provides an updated meta-analysis that includes data from two new randomized trials. Limitations of the study include heterogeneity in antithrombotic therapy and device type, heterogeneity and inconclusiveness of atrial fibrillation (AF) results, and low numbers for some results.
Click to read the study in Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Closure or medical therapy for cryptogenic stroke with patent foramen ovale
In-Depth [systematic review and meta-analysis]: The authors used PubMed and the Cochrane Library, abstracts from major cardiology meetings, reference lists, and ClinicalTrials.gov to find randomized controlled trials with adult enrollees who had PFO and cryptogenic stroke. The authors evaluated potential harms and stroke outcomes for patients who had a transcatheter device closure compared to those who received only medical therapy. The authors found 4 trials that were of high-quality and included a total of 2 892 patients. These trials included PC (2013), RESPECT Extended (2017), CLOSE (2017), and REDUCE (2017). These trials indicated that PFO closure reduced recurrent stroke risk by 3.2% in comparison to medical therapy alone. The treatment methods had no difference in rates of major bleeding or transient ischemic attack. PFO closure was linked to increased rates of atrial fibrillation (AF) compared to medical therapy alone. The authors considered these results to be inconclusive due to significant heterogeneity between trials and high event rates in some groups that caused some confidence intervals to have extreme values. However, the authors also stated that AF risk is a serious safety concern that patients should be notified of as a possibility.
Image: PD
©2018 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.