Prognostic value demonstrated for change of circulating tumour cells and human leukocyte antigen I: programmed cell death-ligand 1 ratio in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
1. Reduced median overall survival associated with annual rate of change in circulating tumour cell (CTC) abundance >0.12 CTCs/mL
2. Decreased median overall survival for patients with an human leukocyte antigen I: programmed cell death-ligand 1 ratio ratio trajectory ≥ 0.0012 annually
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is complicated by the evolution of disease resistance to most first line treatment options, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and tyrosine kinase (TKI) inhibition, and immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). It is postulated that the downregulation of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) I, a complex of genes that encode proteins that regulate the immune system, has been attributed to immune evasion in cancer, as has the upregulation of programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), a transmembrane protein that suppresses the immune system. The use of a peripheral blood sample to track circulating tumour cells (CTCs) can be used to monitor and manage response to treatment. This study aimed to show the utility of monitoring patients longitudinally by investigating the molecular evolution of mRCC to TKIs and ICBs using the rate of change of circulating tumour cell (CTC) abundance over time. Additionally, the study authors hypothesized that the log-ratio of HLA I to PD-L1 (HP ratio) could provide real time insight into variations of the immune cell composition, determined by the slope of a global linear model, during ICBs. The results showed patients in the immunotherapy cohort had a significantly shorter overall survival (OS) when the rate of change of their CTCs were greater. HP ratios decreased during ICB but not during TKI therapy which likely reflects the evolution of an immunotherapy-resistant population. Furthermore, the median OS was significantly reduced in patients whose HP ratio trajectory was higher, such as those in the highest quartile of change. Limitations to this study include that the institutional cohort received heterogeneous treatments for their mRCC. Additionally, there was a minority of patients receiving ICB and TKI, so results should be carefully considered in these populations. Overall, both a change in CTC abundance and HP ratio over time had prognostic value and may represent a promising therapeutic monitoring companion with radiographic imaging.
Click to read the study in The Journal of Clinical Oncology
Relevant Reading: Detection of circulating tumour cells before and following adjuvant chemotherapy and long-term prognosis of early breast cancer
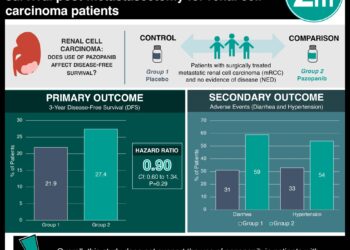
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This study enrolled 104 patients into 2 cohorts: a phase 2, multi-centre, adaptive immunotherapy (OM) group and a prospective institutional cohort based out of the University of Wisconsin (UW). The OM group was comprised of 60 patients, from whom 305 samples were obtained. There were 44 patients in the UW group with 152 samples. In the OM group, the normalized CTC abundance (the number of CTCs divided by volume of blood sample obtained) was between 0 and 718.4 CTCs/mL. This value was between 0.7 and 91.3 CTCs/mL in the UW cohort. For patients in the OM group, those who had an annual rate of change in CTC abundance >0.12 CTCs/mL (highest quartile) had a significantly reduced median overall survival (OS) at 17.2 months, as compared to those who had a rate of change ≤ 0.12 CTCs/mL at 21.1 months (hazard ratio (HR) = 5.9, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.9 to 18.7). The median OS was reduced significantly at 18.35 months for patients with an HP ratio trajectory ≥ 0.0012 annually (highest quartile), as compared to 21.22 months for those with an HP ratio trajectory < 0.0012 (HR = 4.8, 95% CI, 1.5 to 15.3).
Image: PD
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.