Prophylactic tranexamic acid prevents significant blood loss after cesarean delivery
1. Prophylactic tranexamic acid treatment was shown to lower the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage in women undergoing cesarean delivery.
2. Tranexamic acid treatment was shown not to lower the incidence of hemorrhage-related outcomes such as additional uterotonic agent use and postpartum blood transfusion.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Uterotonic agents are often given to avoid significant postpartum hemorrhage. Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic drug that can help prevent significant blood loss in other elective surgeries and may be applicable to cesarean delivery procedures. As such, this study examined the effect of prophylactic tranexamic acid treatment in women undergoing cesarean delivery. The study determined the patients receiving tranexamic acid experienced a lower incidence of significant postpartum hemorrhage compared to the placebo treatment. With respect to secondary outcomes, no significant differences were found in gravimetrically estimated blood loss, excessive bleeding, or additional interventional measures. However, the tranexamic group had lower estimated blood loss and smaller changes in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels post-surgery. This study boasts a large sample size and small exclusion criteria, suggesting high representativeness to the general population. The study was limited by having included emergency cesarean deliveries performed during labor, which increases the likelihood of postpartum hemorrhage. Nonetheless, the study concluded prophylactic tranexamic acid was effective in preventing significant postpartum hemorrhage after cesarean delivery.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Safety and efficacy of tranexamic acid for prevention of obstetric haemorrhage: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
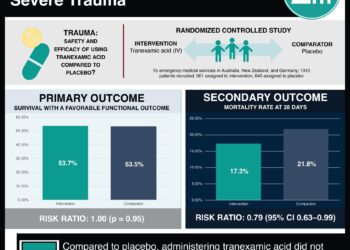
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This randomized control trial enrolled 4,551 women from 27 hospitals in France. Women who were 18 years of age or older, at 34 or more weeks of gestation, and expected to undergo cesarean delivery were included in the study. Women with a history of epilepsy or seizures, increased risk of venous or arterial thrombosis, or poor comprehension of spoken French were excluded from the study. The patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either one milligram of tranexamic acid or placebo, respectively. The primary outcome was postpartum hemorrhage, which was defined as a calculated estimated blood loss over 1000mL or administration of red-cell transfusion within two days of delivery. Overall, 26.7% of women receiving tranexamic acid and 31.6% of women in the placebo group experienced postpartum hemorrhage (adjusted risk ratio, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.75 to 0.94; P = 0.003). No significant differences were found between groups in secondary measures of mean gravimetrically estimated blood loss, provider-assessed significant hemorrhage, or incidence of additional related interventions such as emergency surgery or arterial embolization. Finally, women receiving tranexamic acid reported a higher incidence of vomiting or nausea (P < 0.001), but no differences in thromboembolic-related adverse events were found on follow-up three months later (P = 0.08) between both groups. Altogether, prophylactic tranexamic acid was shown to be effective in lowering the incidence of postpartum hemorrhage after cesarean delivery.
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.