Quick Take: Association of Systemic Antibiotic Treatment of Acne With Skin Microbiota Characteristics
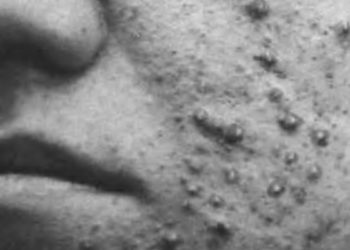
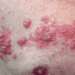
Systemic antibiotics are commonly used in the treatment of acne. However, the impact of their use on the complete bacterial microbiome of skin has not been well studied. In this small cohort study, investigators assessed skin samples from 4 women who were prescribed minocycline across 12 weeks in order to examine the effect of minocycline on the composition, diversity and resilience of skin microbiota associated with systemic antibiotic perturbation in individuals with acne. Investigators found that the mean relative abundance of Cutibacterium acnes decreased for all patients from baseline to week 4 of minocycline treatment (p=0.04). At 8 weeks post-discontinuation of minocycline treatment, the relative abundance of C. acnes had reverted to a level that was not statistically significant from baseline (p=0.06). Investigators found 12 genera of bacteria from skin samples showed statistically significant changes over time and had relative abundance greater than 0.1% in all samples. Five genera showed decreases in relative abundance from baseline to week 4 of treatment: Cutibacterium (p=0.04), Corynebacterium (p=0.005), Prevotella (p=0.008), Lactobacillus (p=0.02), and Porphyromonas (p=0.01). Out of these 5 genera, only Porphyromonas had relative abundances similar to baseline at week 8 after discontinuation of minocycline. There were also 7 genera that demonstrated greater relative abundance from baseline to week 4 of minocycline: Streptococcus (p=0.04), Chryseobacterium (p=0.01), Finegoldia (p=0.03), Pseudomonas (p<0.001), Erwinia (p<0.001), Actinobacillus (p=0.04), and Micrococcus (p=0.03). Streptococcus, Chryseobacterium, Finegoldia species did not have relative levels return to baseline after discontinuation of minocycline. Overall, the results of this study indicate that systemic antibiotic treatment for acne is associated with changes in the composition and diversity of skin microbiota, and variable rates of recovery across individuals. Reductions in the relative abundance of C. acnes along with the concurrent growth and suppression of certain bacterial populations has important clinical implications and may help clinicians in decreasing the likelihood of comorbidities related to microbial dysbiosis.
Click to read the study in JAMA Dermatology
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.