Radiofrequency catheter ablation effective as first-line therapy for atrial fibrillation [RAAFT-2 trial]
Image: PD
1. Radiofrequency catheter ablation is often used after failure of pharmacologic anti-arrhythmic therapy to treat atrial fibrillation.
2. Recurrent atrial fibrillation was less common in patients treated with radiofrequency catheter ablation compared with pharmacological therapy.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: While pharmacological therapies have proven effective in treating atrial fibrillation (AF), studies have shown that almost half of all treated patients have recurrence within the first year. Radiofrequency catheter ablation is an alternative therapy that has proven useful in patients with recurrent AF. The Radiofrequency Ablation vs. Antiarrhythmic Drugs as First-Line Treatment of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (RAAFT-2) study examined the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation as first-line treatment for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) compared to pharmacological management. The study demonstrated a significantly decreased rate of AF recurrence in patients treated with radiofrequency ablation with 2 years of follow-up. Of note, a significant proportion of patients had AF recurrence within two years regardless of randomization.
The study’s strengths lie in its thorough follow-up protocol and its multi-institutional, international patient cohort. Nonetheless, a few limitations should be noted. The pharmacologic therapy was not standardized across all participating nations and they were based on the guidelines set forth by each nation’s governing medical body. Additionally, while follow-up was commendable, there was still a significant proportion of the study cohort that had issues with compliance with regular ECG testing. The sample size was also relatively small, and further study will be required to further explore the use of cardiac ablation as a first-line therapy for AF.
Click to read the study in JAMA
Click to read an accompanying editorial in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Discerning the Incidence of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Episodes of Atrial Fibrillation Before and After Catheter Ablation
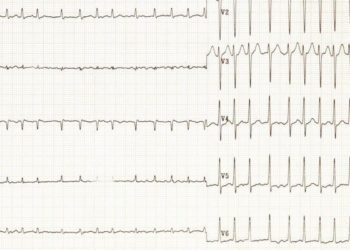
In-Depth [randomized clinical trial]: Patients were selected from Canada, Germany, Italy, Czech Republic, and the United States. Patients were between the ages of 18 and 75, had a history of paroxysmal AF, less than 4 events each lasting more than 30 seconds, and were not previously exposed to antiarrhythmic treatments. Patients were treated and then see in follow-up at 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 months following treatment. Additionally patients reported any symptomatic cardiac events and had biweekly transtelephonic ECG monitoring. The primary outcome was the incidence of any atrial arrhythmia lasting more than 30 seconds. Of the 61 patients treated with either flecainide or propafenone, 44 (72.18%) had recurrent arrhythmia in the 2 years of follow-up. Of the 66 patients who underwent catheter ablation 36 (54.5%) had recurrent arrhythmias with a hazard ratio of 0.56 (CI95%[ 0.35-0.90]) relative to the pharmacological cohort. Secondary outcomes of anxiety depression, visual analog score, and quality of life showed no significant difference between the groups.
More from this author: Vitamin E associated with slower functional decline in Alzheimer disease [TEAM-AD Trial], PET scans accurately identify amyloid deposition following traumatic brain injury, Bystander CPR positively associated with cardiac arrest survival, Terminal cancer patients hold misconceptions of the role of chemotherapy, Home-based walking program an effective treatment for peripheral artery disease
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.