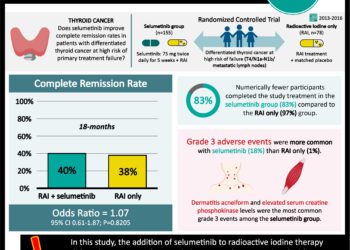
Selumetinib increases the uptake of radioiodine in patients with metastatic thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine
Feb 13th – Published today, 8 out of 20 patients with metastatic thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine therapy trapped therapeutic doses of radioiodine after administration of Selumetinib.
[tabs tab1=”2MM Rundown” tab2= “2MM Full Report”]
[tab]
Image: PD
1. 8 out of 20 patients with metastatic thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine therapy trapped therapeutic doses of radioiodine after administration of Selumetinib.
2. 7 out of 8 of these patients’ thyroid cancer did not progress after 6 months.
The purpose of this translational research was to determine whether patients with metastatic thyroid disease who were refractory to radioiodine therapy could be induced to uptake radioiodine after administration of Selumetinib. The study determined that some patients became responsive to radioiodine therapy and had no progression of their cancer after 6 months of treatment. This study was based on in vivo studies of transgenic mice with thyroid cancer cells that had a constitutive MAPK signaling which inhibited the uptake of iodine. They found the Selumetinib, a MAPK Kinase inhibitor, could induce these cells to uptake iodine.
Although this trial shows very promising data, there are several limitations to this study. One of the major limitations of this study is the use of secondary endpoints. Although the thyroid cancers were responsive to Selumetinib therapy were stable after 6 months, the authors did not explore whether this drug improves mortality. This is however not possible with a sample size of only 8 patients since it would not have enough statistical power. The strengths of this study were the multiple methods used to quantify radioiodine reuptake, as well as extensive genetic analysis of the tumors. Future research should (1) expand the number of subjects and (2) determine why certain mutations were more responsive to Selumetinib therapy.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
[/tab]
[tab]
Image: PD
1. 8 out of 20 patients with metastatic thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine therapy trapped therapeutic doses of radioiodine after administration of Selumetinib.
2. 7 out of 8 of these patients’ thyroid cancer did not progress after 6 months.
This [prospective] study: measured the uptake of radioiodine after administration Selumetinib, a MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitor, in 20 patients with metastatic thyroid cancer who were resistant to radioiodine therapy. Subjects were eligible for the study if the thyroid cancer did not take up radioiodine on imaging, remained stable or progressed after 6 months of treatment, or the masses that had poor uptake of iodine. Patients were assessed of their radioiodine uptake by PET-FDG scan before and after Selumetinib by a radiologist.
Of the 20 patients who were eligible for the study, only 8 of the masses trapped enough radioiodine to be therapeutic after Selumetinib infusion. Of those 8, 5 of the lesions had a NRAS mutation, and the other three had a BRAF, RET/PTC mutation or was wildtype. After 6 months, 7 of patients were stable, but one patient had progression of their thyroid cancer.
In sum: The purpose of this translational research was to determine whether patients with metastatic thyroid disease who were refractory to radioiodine therapy could be induced to uptake radioiodine after administration of Selumetinib. The study determined that some patients became responsive to radioiodine therapy and had no progression of their cancer after 6 months of treatment. This study was based on in vivo studies of transgenic mice with thyroid cancer cells that had a constitutive MAPK signaling which inhibited the uptake of iodine. They found the Selumetinib, a MAPK Kinase inhibitor, could induce cells to uptake iodine.
Although this trial shows very promising data, there are several limitations to this study. One of the major limitations of this study is the use of secondary endpoints. Although the thyroid cancers, which were responsive to Selumetinib therapy were stable after 6 months, the authors have not explored whether this drug improves mortality. This is however not possible with a sample size of only 8 patients. The strengths of this study were the multiple methods used to quantify radioiodine reuptake, as well as extensive genetic analysis of the tumors. Future research should (1) expand the number of subjects and (2) determine why certain mutations were more responsive to Selumetinib therapy.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
By Jeremy Chan and Mitalee Patil
More from this author: A fractional two-dose regimen of the polio vaccine presents a low-cost alternative to the current schedule, Metastatic prostate cancer patients who have not received chemotherapy survive longer on abiraterone plus prednisone,
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.
[/tab]
[/tabs]