#VisualAbstract: Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer
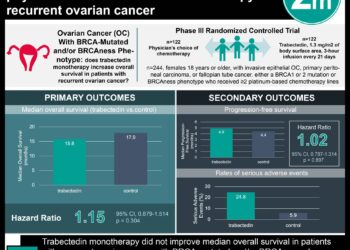
1. Niraparib, a PARP (polyadenosine diphosphate ADP-ribose polymerase) inhibitor, has been associated with an increase in progression-free survival among patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
2. In this phase 3 trial, patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer who received niraparib had a significantly longer progression-free survival than those who received placebo.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Ovarian cancer has a high mortality rate worldwide and up to 85% of those treated with chemotherapy have disease recurrence. Data on bevacizumab maintenance therapy is limited. Olaparib has been associated with longer progression-free survival among patients with BRCA-mutated tumors. Niraparib, a PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor, has been approved for maintenance therapy among patients with recurrent ovarian cancer with and without BRCA mutations. This randomized, phase 3 trial assessed the effect of niraparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer after treatment with a platinum-based chemotherapy. Participants were followed to determine progression-free survival, overall survival, and adverse events of niraparib. The median progression-free survival was higher among patients in the niraparib groups as compared to the placebo groups. In addition, the estimated 24-month survival was higher in the niraparib groups. The most common adverse effects were anemia, thrombocytopenia, and neutropenia. No deaths were reported and no difference in quality-of-life scores were found between the groups. This well-designed trial shows the effectiveness of niraparib as maintenance therapy in preventing ovarian cancer recurrence in patients after receiving chemotherapy. Further research needs to be done to determine the long-term efficacy of niraparib.
Click to read the study in NEJM
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.