Delayed endovascular thrombectomy associated with greater clinical benefit among patients with mismatch imaging profiles in treatment of subacute ischemic stroke
1. The findings supported the use of endovascular thrombectomy in patients who met criteria for either the clinical or target perfusion imaging mismatch profiles, who presented within the 6- to 24-hour since last known well treatment interval for endovascular thrombectomy.
2. The same clinical benefits and reduction in disability associated with endovascular thrombectomy was not observed among patients with underdetermined imaging profiles where further studies are required.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
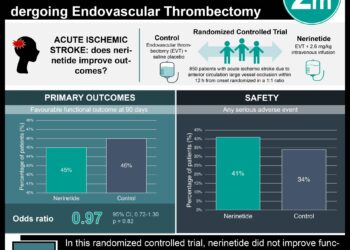
Study Rundown: Although the use of intravenous thrombolytics has been firmly established as the main treatment for acute ischemic stroke presenting within 4.5 hours of symptoms onset, the optimal imaging approach for identifying patients who may benefit from endovascular thrombectomy (EVT), a neurointerventional procedure, past 6 hours of symptoms onset is not well established. This pooled analysis of 6 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) as part of the AURORA Collaboration sought to evaluate the therapeutic benefits of EVT among 3 patient subcohorts with the following baseline imaging profiles: (1) clinical mismatch patients who met the imaging criteria used in the DAWN study (Diffusion Weighted Imaging or Computerized Tomography Perfusion Assessment With Clinical Mismatch in the Triage of Wake Up and Late Presenting Strokes Undergoing Neurointervention), (2) target perfusion mismatch patients who met the imaging criteria used in the DEFUSE 3 study (Endovascular Therapy Following Imaging Evaluation for Ischemic Stroke 3), and (3) undetermined imaging mismatch patients where no adequate perfusion study was performed. The main outcome and measure of the analysis was reduction in disability measured by the modified Rankin Scale at 90 days across the subcohorts and further stratified into 3 acute treatment intervals (tercile 1, 360-574 minutes [6.0-9.5 hours]; tercile 2, 575-762 minutes [9.6-12.7 hours]; and tercile 3, 763-1440 minutes [12.8-24.0 hours]). Among 505 pooled patients with ischemic stroke, treatment via EVT was associated with a reduction in disability among patients in the clinical mismatch (clinical defect vs size of early infarction) and target perfusion mismatch (size of perfusion lesion vs size of early infarction) subcohorts and not observed in stroke patients with an undetermined imaging profile. Thus, performance of EVT provided greater clinical benefit among patients with either of the mismatch imaging profiles compared to those with an undetermined imaging profile. These findings supported the use of EVT in patients who met criteria for either the clinical or target perfusion imaging mismatch profiles who presented within the 6- to 24-hour treatment interval for EVT. Further studies are required to assess and validate the use of EVT among patients with underdetermined imaging profiles. A limitation of this study was the exclusion of patients who received EVT treatment within 6 hours after stroke onset, limiting the generalizability of the study results.
Click to read the study in JAMA Neurology
Click to read an accompanying editorial in JAMA Neurology
Relevant Reading: Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This pooled analysis of 6 RCTs as part of the AURORA (Analysis of Pooled Data from Randomized Studies of Thrombectomy More Than 6 Hours After Last Known Well) Collaboration collectively enrolled 505 eligible patients. Among them, 266 (mean [SD] age, 68.4 [13.8] years; 146 women [54.9%]) were assigned to the EVT cohort and 239 (mean [SD] age, 68.7 [13.7] years; 126 men [52.7%]) were assigned to the control cohort. RCTs on endovascular stroke therapy published between January 2010 and March 2021 were identified via online database search and pooled data was analyzed using mixed-effects modeling with fixed effects for parameters of interest. Inclusion criteria included patients with ischemic stroke who were randomized between 6 and 24 hours after they were last known well. Among 295 patients in the clinical mismatch subcohort, EVT was associated with reductions in disability at 90 days vs no EVT (OR, 3.57; 95%CI, 2.29-5.57; P < .001). Similar reductions in disability associated with EVT were also observed in 359 patients in the target perfusion mismatch subcohort (OR, 3.13; 95%CI, 2.10-4.66; P = .001). Furthermore, clinical benefits of statistical significance were observed in all 3 terciles among both subcohorts, with the highest OR observed for tercile 3 (clinical mismatch subcohort, OR, 4.95; 95%CI, 2.20-11.16; P < .001; target perfusion mismatch subcohort, OR, 5.01; 95%CI, 2.37-10.60; P < .001). Furthermore, 132 patients (26.1%) had an undetermined imaging profile with no significant clinical benefit from treatment (OR, 1.59; 95%CI, 0.82-3.06; P = .17). Finally, the interaction between treatment effects for the mismatch subcohorts compared to the undetermined profile subcohort was statically significant (OR, 2.28; 95%CI, 1.11-4.70; P = .03).
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.