E-cigarettes more effective for smoking cessation than nicotine-replacement therapy
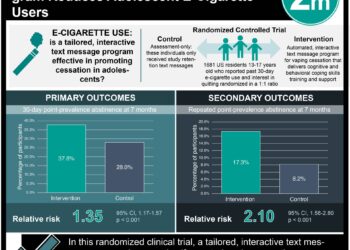
1. At 1 year, patients assigned to e-cigarettes for use in smoking cessation had a higher rate of smoking abstinence compared to those randomized to a nicotine-replacement group when accompanied by behavioral support.
2. Cough and phlegm production decreased from baseline to 1 year to a greater degree in the e-cigarette group compared to the nicotine-replacement group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Smoking cessation is difficult to achieve for many smokers. While complete elimination of smoking and nicotine related product use is ideal, use of e-cigarettes is considered a healthier alternative compared to cigarette smoking. This study sought to compare use of e-cigarettes and nicotine-replacement therapy, both supplemented with behavioral support, for their efficacy in a smoking cessation program. At 1-year, patients randomized to the e-cigarette group had higher rates of smoking cessation compared to patients using nicotine-replacement therapy. Time to relapse rates did not differ between the two groups. Adverse effects of wheezing and shortness of breath were similar between the two groups.
This trial showed e-cigarettes, while not a completely benign treatment, can significantly aid in smoking reduction. Strengths include length of follow-up and tracking of adverse effects, while a notable limitation is the behavioral support program possibly limiting generalizability of the results.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Real‐world effectiveness of e‐cigarettes when used to aid smoking cessation: a cross‐sectional population study
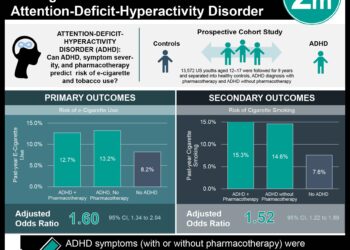
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This multicenter randomized controlled trial enrolled patients in the United Kingdom between 2015 to 2018. Eligible patients were smokers with no preference for e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement and were not using either product at enrollment. Patients were randomized on the first day of smoking cessation to an e-cigarette (n=438) or nicotine-replacement (n=446). All patients received 4 weeks of behavioral support with clinicians. Patients in the nicotine-replacement group were provided with 3 months of product of the patient’s choice (gum, patch, etc.), while those in the e-cigarette group received a starter kit and a nicotine containing refillable container. Patients were followed up to 52 weeks, with the primary outcome being smoking cessation. At 1 year, smoking abstinence rates were 18.0% and 9.9% in the e-cigarette and nicotine-replacement groups, respectively (relative risk [RR], 1.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.30 to 2.58; P<0.001). The number needed to treat to have smoking abstinence at 1-year with use of e-cigarettes was 12 (95% CI, 8 to 27). In patients not at full smoking abstinence, carbon monoxide levels were lower in the e-cigarette group compared to the nicotine group. Time to smoking relapse did not differ between treatment groups. When considering those abstinent of smoking at 1 year, 80% (63/79) of those in the e-cigarette group were actively using their treatment aid, while 9% (4/44) of those in the nicotine group were using a replacement product. Participants rated e-cigarettes as more satisfying and more helpful in refraining from smoking compared to nicotine-replacement products. Of patients that had cough or phlegm at baseline, more e-cigarette users were free of symptoms at 1 year compared to nicotine-replacement users.
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc