H. Pylori infection influenced by genes
Image: PD/Yutaka Tsutsumi, M.D.
1. Individuals with increased expression of Toll-Like Receptor 1 (TLR-1) were more likely to be seropositive for H. Pylori.
2. Genetic testing for H. Pylori is not yet justifiable without establishing clear clinical implications.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: In performing a meta-analysis on 2 independent Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWASs), this analysis indicates that higher expression of Toll-Like Receptor 1 (TLR1) is associated with H pylori seropositivity and higher levels of fecal antigen. It is postulated that this may be possibly due to a lead single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on the locus, which decreases TLR1 signaling efficiency, ultimately contributing to either attaining or retaining the infection. Further studies are needed to better delineate the relationship between exposure to the pathogen and subsequent development of clinical symptoms, as well as the inclusion of non-European populations. Teamed together with additional research into the precise genetic mechanisms responsible for this association, this analysis could potentially be applied to target rising antibiotic resistance and eradication of H pylori to prevent cancer development in the future.
Click to read the study in JAMA
Click to read the accompanying editorial in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Review: Helicobacter pylori infection
In-Depth [meta-analysis]: This study consisted of 2 independent GWASs and meta-analysis of anti-H pylori IgG serology that was prospectively collected in large German and Dutch cohorts, in addition to whole-blood RNA gene expression profiles and fecal H pylori antigen. Of the total 10,938 participants (2763 cases and 8175 controls), 56.3% were seropositive for H pylori. TLR (Toll-Like Receptor) locus, specifically TLR-1, and FCGR2A (Low affinity IgG Fc region receptor II-a) locus were statistically significantly and associated with seroprevalence (p=1.4 x 10-18 and p=2.1×10-8 respectively). Interestingly, individuals with high levels of fecal H pylori antigen expressed TLR1 at the highest 25% range (P=0.01) and only TLR1 was differentially expressed per copy number of the lead SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) rs10004195-A minor allele of the TLR locus.
By Elizabeth Park and Rif Rahman
More from this author: Trigger exposure in migraine patients results in migraine with aura only in a small subset of patients, Choosing a prenatal diagnostic test: Microarray analysis shown equal to karyotyping,STEMO unit delivery of tpa reduces call to needle time in acute stroke patients,High-dose multivitamin supplements do not decrease disease progression or death in HIV patients receiving HAART ,Pediatric patients not receiving quality palliative care despite agreement between parents and caregivers on valued elements of care ,Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic melanoma significantly improves progression free survival
© 2013 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.


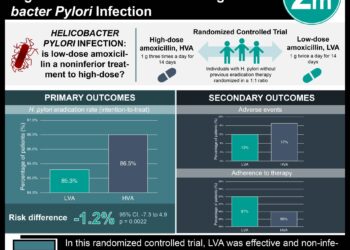


![Pointed techniques: an experience of acupuncture and western medicine [Perspective]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/Hua_t08-75x75.jpg)