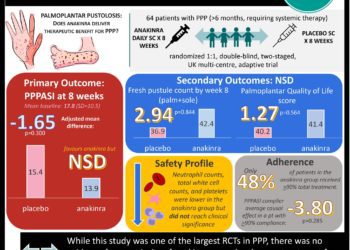
Open-label placebo effective therapy for children with functional abdominal pain or irritable bowel syndrome
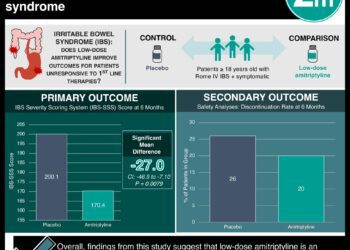
1. In a crossover randomized controlled trial of 30 children with functional abdominal pain or irritable bowel syndrome, patient-reported pain scores decreased slightly but significantly with an open-label placebo.
2. Patients’ use of rescue pain medication was also significantly lower during use of the placebo.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Disorders of gut-brain interaction such as functional abdominal pain and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are often chronic and difficult to treat due to a lack of identified organic targets. In several double-blinded studies of medications in children with these disorders, there is a high rate of favorable response amongst those receiving placebo. This multicenter, crossover study is the first to examine the efficacy of an open-label placebo in a pediatric population. 30 participants were randomized to undergo a 3-week control period either before or after taking a placebo sugar suspension twice daily for 3 weeks. All patients were given hyoscyamine tablets as an as-needed rescue pain medication. Patient-reported daily pain scores were significantly lower during the placebo than the control period, and patients required fewer doses of rescue medication. There were no significant patient-reported differences in bowel movements between periods. This study shows a small but convincing effect of open-label placebo on pain associated with functional abdominal pain and IBS in children. Generalizability is limited by the very small sample size. Physicians in this study used a standardized script to explain the nature of the placebo and its potential benefits based on past studies. This could potentially contribute to the placebo effect observed in this study, but could also be readily reproduced in clinical practice.
Click to read the study in JAMA Pediatrics
Relevant Reading: Pediatric functional abdominal pain disorders
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: Children aged 8 to 18 (n=30) with moderate to severe pain due to either functional abdominal pain or IBS, diagnosed using Rome III criteria, were included. 80% were female. 53.3% had functional abdominal pain and 46.7% had IBS. Patients who had been taking stable pain regimens for more than 30 days were permitted to continue these regimens. Mean daily pain scores reported using a visual analog scale were 39.9 during the placebo period and 45.0 during the control for a difference of 5.2 (95% confidence interval 0.2-10.1, p = 0.03). 70% of patients had lower average pain scores during the placebo period. Based on counting of remaining tablets at the end of each study period, patients used 3.8 tablets on average during the placebo period and 2.0 during the control period for a difference of 1.8 tablets (0.5-3.1, p < 0.001). 14 patients reported overall improvement during the placebo period, while 9 reported improvement during the control period. 13 patients reported an expectation that the placebo would improve their symptoms; there was no significant correlation between expectation and reported global improvement.
Image: PD
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.