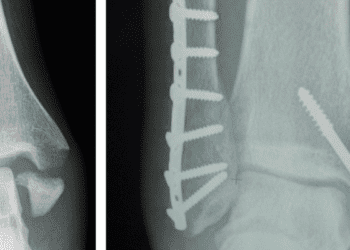
Outcomes similar for operative vs nonoperative treatment for acute unstable chest wall injuries
1. In this randomized controlled trial, there was no significant difference in ventilator-free days (VFDs) in the first 28 days after injury in patients who received either operative or nonoperative treatment for an unstable chest wall injury.
2. In patients who were mechanically ventilated at the time of randomization, operative treatment resulted in a significantly shorter length of in-hospital stay versus nonoperative treatment.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Chest wall injuries causing instability from blunt chest trauma have high rates of mortality and morbidity; with high incidence of complications including chest wall instability and pulmonary complications. The most prevalent treatment is nonoperative, including intubation, positive pressure ventilation, pain control, and chest physiotherapy. However, this nonoperative approach may not produce optimal results. Previous research has reported improved outcomes with an operative versus nonoperative approach, but there is a paucity of high-quality randomized-controlled trials comparing these approaches. This multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled trial compared operative treatment of unstable chest wall injuries with nonoperative management. Patients were randomized to either receive operative or nonoperative treatment of their chest wall injury. The primary outcome was the number of ventilator-free days (VFDs) during the first 28 days following injury. 211 patients were recruited from 15 level 1 trauma centers across Canada and the United States from October 2011 to September 2018 meeting an indication for surgical fixation of chest wall injury. 111 patients were randomly assigned to receive operative treatment, and 100 patients were randomly assigned to receive nonoperative treatment. With respect to the primary outcome, mean VFDs were 22.7 days for the operative group, and 20.6 days for the nonoperative group (mean difference 2.1 days; 95% CI, -0.3 to 4.5 days; P=.09). However, in patients who were ventilated at the time of randomization, operative treatment reduced length of stay in hospital (HR, 1.4; 95% CI, 0.9 – 2.1) when compared to nonoperative treatment, while the number of VFDs were still similar between the two groups. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups with respect to VFDs or number of days receiving mechanical ventilation. For secondary outcomes, there were no differences in length of hospital or ICU stay between groups, similar rates of complications, and rates of pneumonia, sepsis, and tracheostomy. A major limitation of this study was the sample size; though it was one of the largest randomized controlled trials to date of this type, it was underpowered to detect statistical significance in certain outcomes. Overall, the findings of this study suggest no difference in operative versus nonoperative treatment in patients with acute unstable chest wall injuries with respect to VFDs and complications. However, within the subgroup analyses, there was a possible benefit of operative treatment in patients receiving mechanical ventilation at the time of randomization, resulting in a significantly shorter in-hospital stay. Further investigation is required, particularly more randomized controlled trials, to adequately compare operative versus nonoperative treatment in acute unstable chest wall injuries.
Click to read the study in JAMA Surgery
Image: PD
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.