Quality improvement initiative in pediatric emergency departments improves opioid prescribing practices
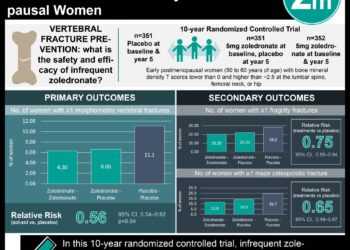
1. In this multi-center quality improvement study, opioid prescriptions in pediatric emergency departments for extremity fracture or cutaneous abscess drain significantly decreased, with no increase in the number of return visits for uncontrolled pain.
2. Uptake of physician enrollment in a prescription drug monitoring program and provision of discharge instructions for safe opioid storage and disposal to patients increased to 100%.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Opioid misuse can lead to adverse events, including overdose and death. Variability in opioid prescribing, as well as overprescribing due to a lack of evidence-based guidelines, are important contributors to opioid availability. The current study aimed to implement quality improvement (QI) initiatives in pediatric emergency departments (EDs) in order to provide appropriate analgesia to patients discharged from the ED while standardizing opioid prescribing and educating physicians as well as families regarding safe storage and disposal of opioids. QI initiatives aimed to decrease opioid prescriptions to 8%, reduce opioid prescriptions of >3 days to 10%, avoid codeine prescriptions, enroll all ED physicians in the prescription drug monitoring program (PMP), and increase safe opioid storage and disposal discharge instructions to 70%. Opioid prescriptions significantly decreased after QI implementation from 13% to 7%, codeine prescriptions dropped to 0%, all ED physicians enrolled in the PMP, and opioid storage and disposal instruction dissemination significantly increased. There was no significant difference in the number of return visits for uncontrolled pain compared to the baseline period prior to the intervention period. Although this study is limited to two common pediatric presentations and did not investigate whether opioid prescriptions were actually filled, it demonstrates that multidisciplinary QI initiatives can improve opioid stewardship in pediatric EDs.
Click to read the study in PEDIATRICS
Relevant Reading: Opioid prescribing to US children and young adults in 2019
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This quality improvement study included 3 pediatric EDs in tertiary-care children’s hospitals near Houston, Texas, between May 2018 and April 2020. Multidisciplinary teams discussed barriers to opioid stewardship and identified six educational goals: using nonopioid analgesic alternatives, avoiding codeine prescriptions, enrolling physicians in PMP, limiting opioid prescriptions, avoiding opioid prescriptions >3 days unless necessary, and providing safe storage and disposal instructions after opioid prescription. In total, 3402 children aged 0 to 18 with an extremity fracture or drainage of a cutaneous abscess were included in the study. Visits to the ED or clinic (i.e., primary care or orthopedic) <3 days after discharge due to uncontrolled pain were evaluated. Compared to baseline visits in 2017, opioid prescriptions decreased from 13% to 7% (p<0.0001), >3 day opioid supply decreased from 41% to 13% (p<0.0001), codeine prescriptions dropped from 1.1% to 0% (p=0.09), and physician enrollment in the PMP as well as discharge instructions increased from 0% to 100% (p,0.0001). There was no difference in return visits for uncontrolled pain when comparing baseline to the intervention.
Image: PD
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.