Quick Take: Effect of basal insulin supplement therapy on diabetic retinopathy in short‐duration type 2 diabetes
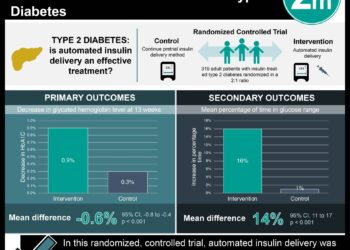
Better treatments are needed for diabetic retinopathy (DR), a microvascular complication of diabetes. Intensive glycemic treatment can delay DR onset and progression, but it is unclear whether oral anti-diabetic drugs alone (OADs) or basal insulin-supported OADs are superior in terms of subsequent treatment. Traditionally, proliferative DR has been regarded as an indication for insulin therapy, however, some recent reports have suggested that insulin therapy is harmful in DR. In this randomized controlled trial, investigators randomized 290 patients with type 2 diabetes to receive either OADs alone or basal insulin-supported OADs (BOT) in order to compare the effect on DR with these types of subsequent therapies. Investigators found that at 12 months, 6.06% of patients in the BOT group had developed DR as compared to 8.3% of the OAD only group (p=0.034). Patients in the BOT group also had lower fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels, 2-hour post-prandial blood glucose (2h-PBG), and HbA1c levels at 6 and 12 months (p<0.05). In terms of adverse effects, similar hypoglycemia rates occurred in the two groups (9.87% for BOT vs. 10.71% for OAD only). Results from this study therefore suggest that adding basal insulin to OADs may help in reducing the risk of developing DR in patients with type 2 diabetes and improve glycemic control. This study was limited in that follow-up time for DR was limited to 12 months, a relatively short time given the chronic nature of diabetes and DR as a microvascular complication.
Click to read the study in Journal of Diabetes
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.