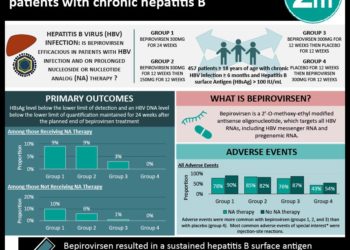
Risk of HBV reactivation associated with rituximab-containing chemotherapy
1. HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc-positive patients in endemic populations undergoing rituximab-containing chemotherapy had a high rate of HBV reactivation.
2. Baseline undetectable HBsAg antibody level (<10 mIU/mL) was the only risk factor associated with reactivation of HBV.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: Immunosuppressive therapy has been previously associated with viral reactivation among patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections. Patients who are HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc positive may have had previously resolved or occult infection with potential for reactivation. Previous retrospective studies have found large variations with regards to the risks of reactivation in this population. The purpose of this study was to provide prospective data on the risk of HBV reactivation in patients with occult/chronic HBV infections undergoing immunosuppressive therapy.
This trial prospectively followed 63 HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc-positive Chinese patients who underwent rituximab-containing therapy. After a median follow-up of 70 weeks, the authors found that the 2-year risk of HBV reactivation in this population cohort was 41.5%. When stratified by baseline HBsAg antibody level, having undetectable (<10 mIU/mL) levels of anti-HBsAg antibodies was significantly associated with HBV reaction (up to 68% risk at 2 years). The study had a strict definition of HBV reactivation (HBV DNA >10 IU/mL), and all cases of reactivation were successfully controlled by administration of entecavir. The results of this trial suggests that patients with chronic HBV infections are at increased risk of reactivation when undergoing rituximab-based chemotherapy. Furthermore, it supports the use of prophylactic antiviral therapy for patients at increased reactivation risk—patients with undetectable anti-HBsAg-antibodies. However, this study was underpowered, only included Chinese patients, and may not reflect the reactivation patterns in patient populations in non-endemic regions.
Click to read the study in Journal of Clinical Oncology
Relevant Reading: Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Lymphoma Patients With Prior Resolved Hepatitis B Undergoing Anticancer Therapy With or Without Rituximab
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This prospective observational study enrolled a total of 64 HBsAg-negative, anti-HBc-positive Chinese patients being treated with rituximab-containing chemotherapies for hematologic malignancies. All patients had undetectable serum HBV DNA at baseline. Patients were monitored every 4 weeks up to 2 years (median follow up: 70 weeks). The primary end-point was HBV reactivation, defined as detectable HBV DNA >10IU/mL. Secondary endpoints were HBsAg positivity at reactivation, ALT elevation at reactivation, and overall survival. Patients with biochemical evidence of reactivation were started on entecavir 0.5mg/day until 12 months after cessation of chemotherapy. Overall, the cumulative rate of HBV reactivation at 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years were 22.6%, 29.4%, and 41.5%, respectively. The median HBV DNA level at reactivation was 43 IU/mL (range: 14-290 IU/mL). Serum ALT were normal for all patients with HBV reactivation. Multi-variate analysis demonstrate that the only significant risk factor for reactivation was a baseline undetectable antibody to HBsAg (HR 3.51, 95% CI, 1.37-8.98, p = 0.009).
More from this author: Rituximab linked with reduced chronic immune disease following stem cell transplantation, High-dose prophylaxis for hemophilia increases costs with minimal benefit, Ambrisentan found ineffective against idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.