Ultrasound as effective as CT at identifying high-risk kidney stones, reduces radiation exposure
1. Point-of-care (POC) ultrasound was equally effective as CT scan in identifying renal calculi at “high-risk” for complications at 30-days after assessment.
2. POC ultrasound reduced radiation exposure at the time of assessment in the emergency department as compared to CT scan.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Renal stones, or calculi, are a common cause for acute pain (“renal colic”) and presentations to emergency departments. Patients with suspected calculi or a history of stones are often exposed to frequent CT scans, thus increasing their radiation exposure. POC ultrasound has recently become more accessible and has the additional benefit of reduced radiation exposure. This modality could be an easier and faster method in the evaluation of renal calculi.
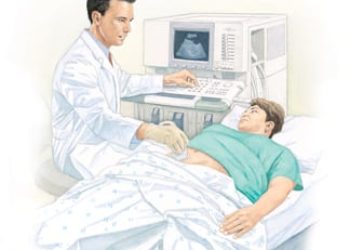
This study randomized patients who presented to emergency departments with suspected renal calculi to one of three initial imaging modalities: point-of-care ultrasound by emergency physician, ultrasound by radiologist or CT scan by technician. Ultrasound (whether by ER physician or radiologist) was found to be as effective as CT scan in identifying stones with “high-risk complications” at 30 days after randomization. Ultrasound was also associated reduced total radiation exposure.
This study could not be blinded and a significant portion of patients randomized to POC or radiologist ultrasound still went on to have a CT scan for various indications. Furthermore, CT scan remained the most sensitive imaging modality for renal calculi when compared to POC and radiologist ultrasound. There is still ongoing analysis as to whether POC ultrasound is more cost effective than CT scan. Overall, the positive results of this study suggest that ultrasound may be a useful tool in the initial evaluation of nephrolithiasis in the emergency setting. Further evaluation is needed to analyze the overall benefit of using POC ultrasound. The feasibility of adopting this method also depends on the training of emergency physicians in using the technology.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
Click to read an accompanying editorial in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Nonenhanced Helical CT and US in the Emergency Evaluation of Patients with Renal Colic: Prospective Comparison
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: 2759 patients with suspected renal calculi from various centers were randomized to one of the following initial imaging modalities: point-of-care ultrasound by emergency physician, radiologist ultrasound, or CT scan. Baseline characteristics were well-matched in all three groups including those with a history of renal calculi and physician “estimated likelihood” of renal calculi.
The primary outcomes of the study were: high risk diagnoses complications that could be related to missed or delayed diagnoses, cumulative radiation exposure from imaging, and total costs. No significant difference in high risk complications was found between the three groups (p=0.30). Radiation exposure during emergency visit at time of enrolment was significantly less in POC ultrasound and radiologist ultrasound groups (p<0.001). Secondary outcomes also demonstrated that POC ultrasound (compared to CT scan) decreased the median duration of emergency room visits (p<0.001) without changing the number of patient returning to emergency (p=0.77) or requiring re-admission to hospital at 60 days follow up (p=0.80).
More from this author: Brodalumab effective in treating active psoriatic arthritis, Idelalisib plus rituximab improves progression-free survival in relapsed CLL, SSRI use during pregnancy not linked to increased risk of autism,Combo antifungal therapy most effective treatment for cryptococcal meningitis
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.