#VisualAbstract: Adjuvant pembrolizumab increased disease-free survival in completely resected, PD-L1 unselected non-small-cell lung cancer patients
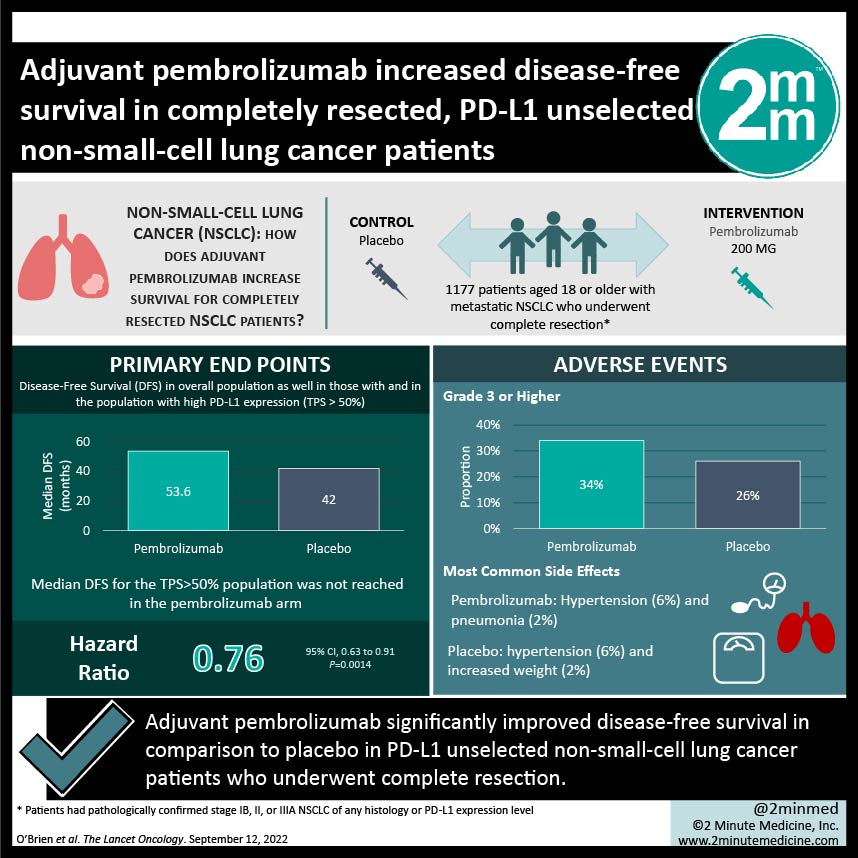
1. Adjuvant pembrolizumab significantly improved disease-free survival in comparison to placebo in PD-L1 unselected non-small-cell lung cancer patients who underwent complete resection.
2. Adverse events of grades 3 or higher occurred slightly more often in the pembrolizumab arm, with the most common ones being hypertension and pneumonia in the pembrolizumab arm and hypertension and weight gain in the placebo arm.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Pembrolizumab (a programmed cell death 1 inhibitor) is the standard of care for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) due to its clinical benefit and tolerable safety profile. This study explored pembrolizumab as an adjuvant therapy for completely resected NSCLC; this is the 2nd interim analysis of the study. Patients who underwent complete resection were randomly assigned to receive either pembrolizumab or placebo as adjuvant therapy. Randomization was stratified by disease stage and PD-L1 tumour proportion score (TPS) among other factors. Median disease-free survival (DFS) was higher in the pembrolizumab arm in the overall population but was not reached in either arm of the TPS>50% population. Overall survival data is still immature at the time of this interim analysis. Adverse events of grades 3 or higher occurred slightly more frequently in the pembrolizumab arm, with the most common in the pembrolizumab arm being hypertension and pneumonia, and hypertension and weight gain in the placebo arm. Serious adverse events occurred slightly more frequently in the pembrolizumab arm, as did treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) that led to death. The strengths of this study are its limited bias given the design and that the results of the study support the current evidence of immune checkpoint inhibitors as adjuvant therapy. Limitations to this study include a predominantly male population and the lack of biomarker use such as EGFR and ALK. Median DFS in the TPS>50 subgroup was also not reached, despite relative benefit of pembrolizumab increasing with increased PD-L1 expression, suggesting that a longer follow-up is also needed. Overall, adjuvant pembrolizumab is a potentially viable treatment option for stage IB-IIIA NSCLC patients who underwent complete resection, regardless of their PD-L1 expression.
Click to read the study in The Lancet Oncology
Relevant Reading: Adjuvant chemotherapy, with or without postoperative radiotherapy, in operable non-small-cell lung cancer: two meta-analyses of individual patient data
In-Depth [randomized control trial]: This international phase III clinical trial included 1177 patients with metastatic NSCLC who underwent complete resection. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either pembrolizumab or placebo as adjuvant therapy; 590 were in the former arm and 587 were in the latter arm. Median DFS in pembrolizumab and placebo arms for the overall population was 53.6 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 39.2 to not reached) and 42.0 months (31.3 to not reached), respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; 95% CI, 0.63 to 0.91; P=0.0014). Median DFS for the TPS>50% population was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm (95% CI, 44.3 to not reached) or the placebo arm (95% CI, 35.8 to not reached) (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.57 to 1.18; P=0.14). Adverse events of grade 3 or higher occurred in 34% of patients in the pembrolizumab arm and in 26% in the placebo arm. Hypertension (6%) and pneumonia (2%) were the most common in the pembrolizumab arm, in comparison to hypertension (6%) and increased weight (2%) in the placebo arm. Serious adverse events occurred in 24% and 15% of patients, respectively. TRAEs that led to death occurred in 1% and 0% of patients, respectively. Immune-mediated events and transfusion reactions occurred in 39% of patients and 13% of patients, respectively. Overall, adjuvant pembrolizumab significantly increased DFS in PD-L1 unselected, completely resected NSCLC patients.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.