#VisualAbstract: Continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes results in improved blood glucose levels
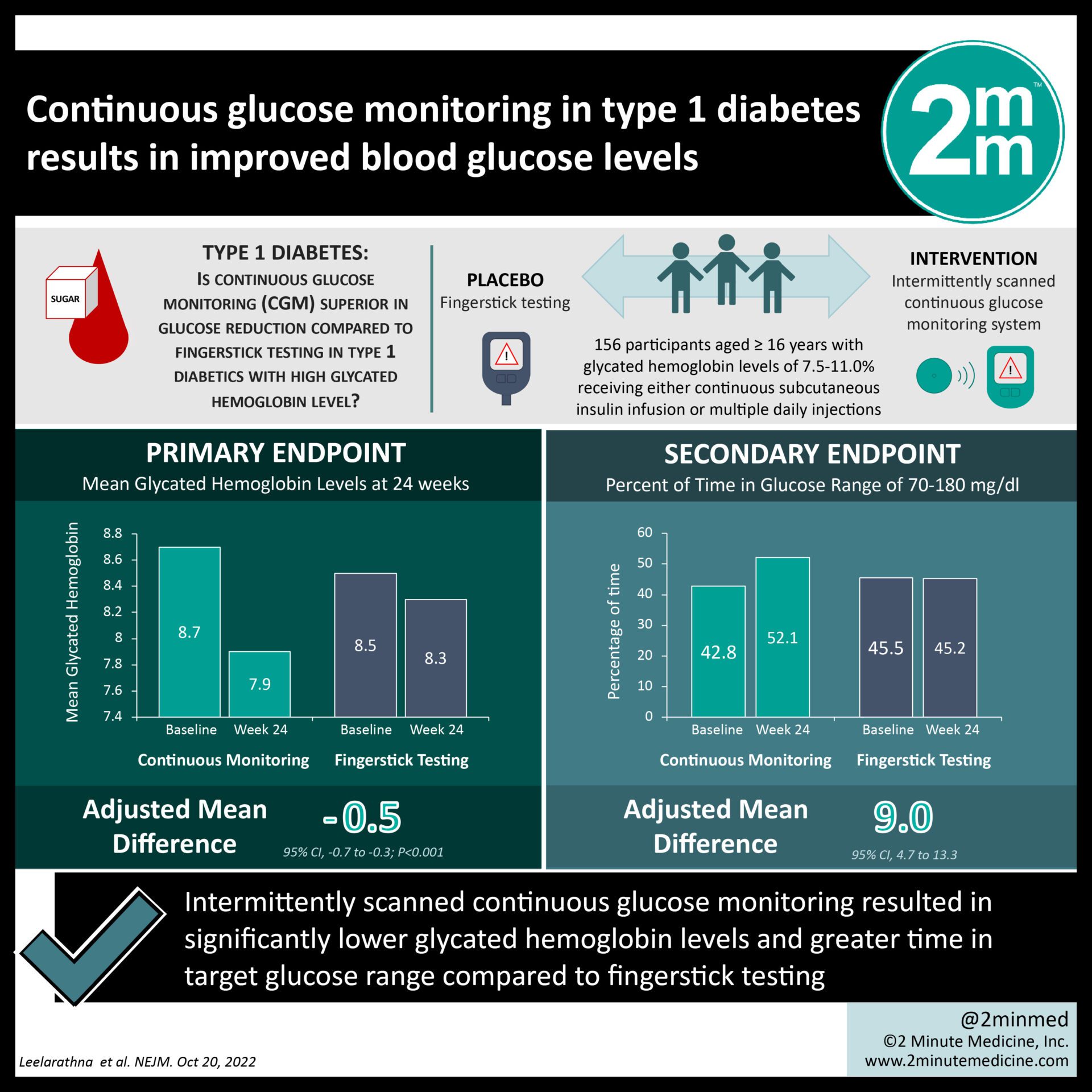 1. In patients with type 1 diabetes, using intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring resulted in significantly lower glycated hemoglobin levels than levels monitored by fingerstick testing.
1. In patients with type 1 diabetes, using intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring resulted in significantly lower glycated hemoglobin levels than levels monitored by fingerstick testing.
2. Intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring led to glucose levels being in the target range for longer than compared to regular fingerstick testing.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: The development of continuous glucose monitoring systems has enabled the monitoring of glucose levels without fingerstick testing. However, there is a gap in knowledge as to understanding the efficacy of intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring with optional alarms for high and low blood glucose levels in persons with type 1 diabetes, as compared with traditional monitoring of blood glucose levels with fingerstick testing. Overall, this study found that those who underwent intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring with optional alarms for high and low blood glucose levels had significantly lower glycated hemoglobin levels than those who monitored their own blood glucose levels with the use of regular fingerstick testing. This study was limited by participants being aware of trial-group assignments, and that nearly all the participants were White, which limits the generalizability of the findings. Nevertheless, these study’s findings are significant, as they demonstrate that continuous glucose monitoring led to a significantly lower glycated hemoglobin level than those who used fingerstick testing to monitor their glucose levels.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Six-Month Randomized, Multicenter Trial of Closed-Loop Control in Type 1 Diabetes
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This parallel-group, multicenter, randomized controlled trial studied participants at seven specialist diabetes clinics and one primary care center in the United Kingdom. Patients who were at least 16 years of age, had type 1 diabetes for at least one year, and had a glycated hemoglobin level of 7.5% to 11.0% while receiving either continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion or multiple daily injections were eligible for the study. Patients who had a current use of a continuous glucose monitor for more than four weeks within the previous 12 weeks, pregnancy or planned pregnancy, and complete loss of awareness of hypoglycemia were excluded from the study. The primary outcome measured was the glycated hemoglobin level at 24 weeks. Outcomes in the primary analysis were assessed via the intention to treat principle and using a linear mixed model. Based on the primary analysis, a total of 156 participants were randomly assigned to undergo intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (intervention group) or to monitor their own blood glucose with fingerstick testing (control group). The mean baseline glycated hemoglobin level was 8.7±0.9% in the intervention group and 8.5±0.8% in the control group. These levels decreased to 7.9±0.8% and 8.3±0.9%, respectively, at 24 weeks (adjusted mean between-group difference, −0.5%; 95% Confidence Interval [CI], −0.7 to −0.3). The glucose level in the target range was 9% higher (95% CI, 4.7 to 13.3) or 130 minutes longer (95% CI, 68 to 192) in the intervention group than in the control group. Time spent in the hypoglycemic state was 43 minutes shorter in the intervention group than in the control group (95% CI, 20 to 65). In summary, this study demonstrated that in patients with type 1 diabetes and high glycated hemoglobin levels, using an intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitor resulted in significantly lower glycated hemoglobin levels than monitoring with regular fingerstick testing.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.