#VisualAbstract: Hydroxyurea dose escalation for sickle cell anemia in sub-Saharan Africa
1. Children with sickle cell disease who received the maximum tolerated dose of hydroxyurea had higher concentrations of hemoglobin and fetal hemoglobin compared to those who received the fixed standard dose.
2. Patients in the dose escalation group also had fewer adverse events and required fewer key medical interventions than their lower dose counterparts.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Hydroxyurea is a myelosuppressive agent that is widely used in the treatment of sickle cell disease. While numerous studies have demonstrated the drug’s efficacy in promoting synthesis of beneficial fetal hemoglobin as well as mitigating the chronic inflammation associated with sickling, dosing standards remain variable across the globe due to safety concerns, especially in groups with limited access to laboratory testing. This study tested the limits of the drug’s therapeutic window and concluded that hydroxyurea with dose escalation proved to be superior to fixed-dose hydroxyurea. Until personally optimized dosing based on pharmacokinetic data is available in low-resource settings, stepwise escalation may be a feasible way to improve clinical outcomes without compromising patient safety. Cost-effectiveness analyses should be conducted to assess whether these benefits justify the costs of an increased drug supply and more intensive monitoring.
Click here to read the study, published in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Hydroxyurea for Children with Sickle Cell Anemia in Sub-Saharan Africa
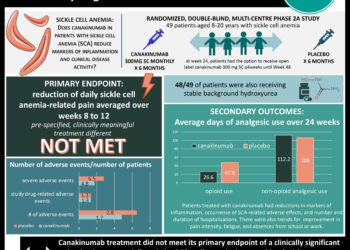
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study included children in Uganda who had previously completed the NOHARM placebo-controlled trial of hydroxyurea treatment. In this NOHARM MTD trial conducted from mid-2017 to early 2020, 187 of the original 207 children were matched according to demographic and clinical characteristics and randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to begin receiving hydroxyurea at a dose of either 20 mg per kg per day or 25 mg per kg per day. The latter group’s dose was escalated by 5 mg per kg per day every 2 months until dose-limiting cytotoxic effects (hemoglobin <4 g/dL, reticulocytes >8 x 1010 g/L, neutrophils <1 x 109 g/L, platelets <8 x 1010 g/L) were observed. At the eighth month, the dose escalation group’s actual mean dose was 29.5±3.6 mg per kg per day, compared to 19.2±1.8 mg per kg per day for the fixed-dose group. After 146 children had completed 18 months of treatment, the trial was terminated due to the clear superiority of dose escalation. At that point, 86% of the dose escalation group had a hemoglobin level of >9.0 g/dL or a fetal hemoglobin level of >20%, versus only 37% of the children assigned to the fixed-dose group (P<0.001). Further, the dose escalation group also had far fewer sickle-cell related adverse events (105 vs. 245; incidence rate ratio [IRR], 0.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.34 to 0.54), transfusions (34 vs. 116; IRR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.20 to 0.43), and hospitalizations (19 vs. 90; IRR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.34) compared to the control group.
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.