
Want more physician-written
medical news?
Join over 10 million yearly readers and numerous companies. For healthcare professionals
and the public.
Subscribe for free today!
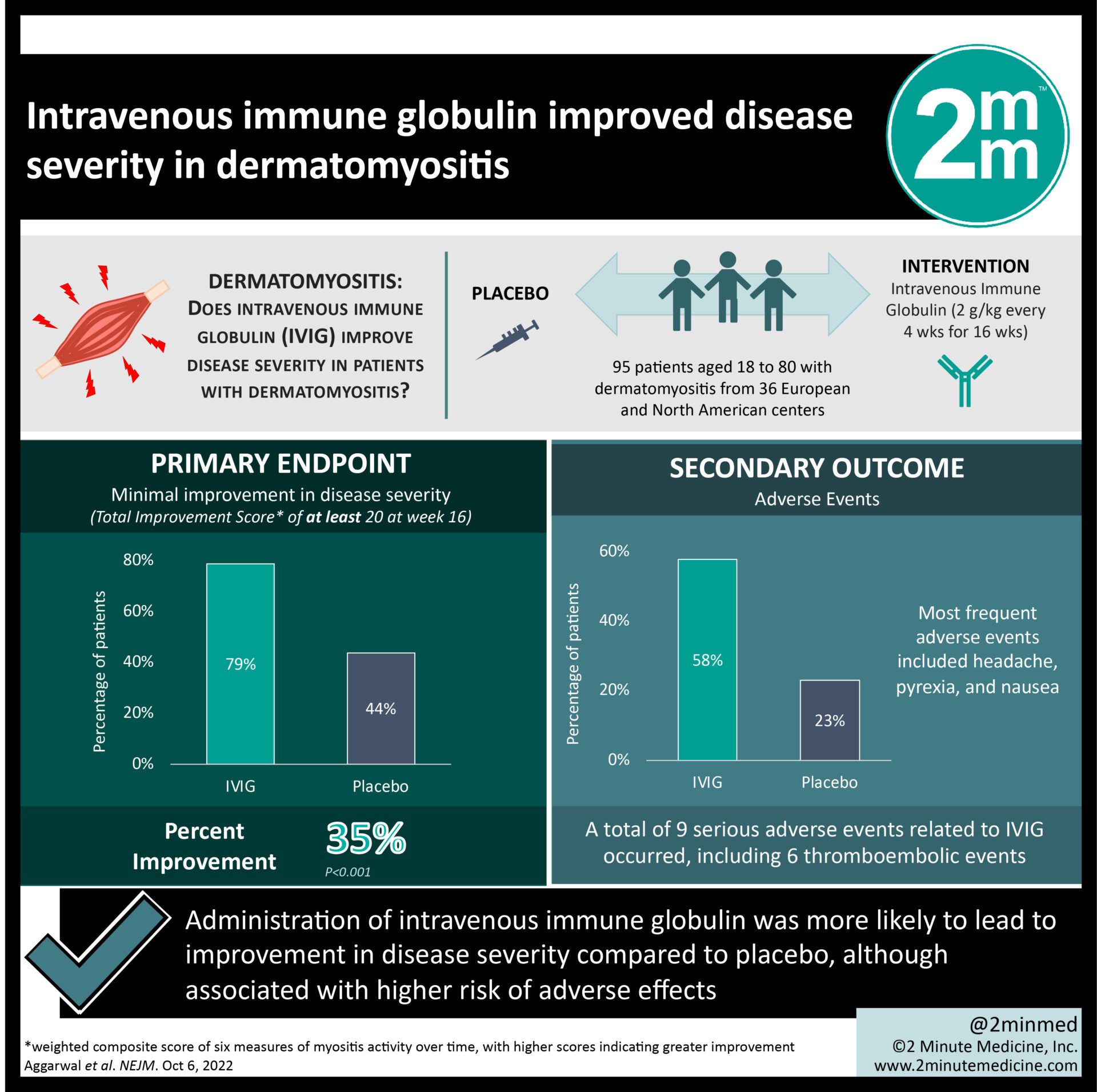 1. Patients with dermatomyositis treated with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) were more likely to see improvement in their disease severity compared to placebo at 16 weeks of follow-up.
1. Patients with dermatomyositis treated with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) were more likely to see improvement in their disease severity compared to placebo at 16 weeks of follow-up.
2. Treatment with IVIG reduced the need for concomitant treatments such as glucocorticoids in patients with dermatomyositis.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Dermatomyositis is characterized by chronic inflammation affecting the skin and muscles, which leads to rashes and progressive muscle weakness. IVIG is currently approved by various regulatory agencies around the world as a second-line treatment for dermatomyositis. A response of minimal improvement was significantly higher in the IVIG group compared to a placebo at 16 weeks. In subgroup analyses, the IVIG group had more improvements with more severe disease. However, these analyses were underpowered. A response of moderate and major improvement was higher in the IVIG group compared to the placebo at 16 weeks. After the open-label extension phase, the percentage of patients with minimal improvement was similar between both groups. The total improvement score (TIS) was similar between both groups after the placebo group was given IVIG by week 40. Patients receiving concomitant glucocorticoid treatment were able to decrease or discontinue the treatment after receiving IVIG. During the placebo-controlled phase, three patients in the placebo group and no patients in the IVIG had clinical deterioration. Adverse events occurred at a higher rate in the IVIG group, most commonly headache, pyrexia, and nausea. Due to the low threshold for minimal improvement, the high rate of response in the placebo group could describe a natural timeline of dermatomyositis that was also seen in the IVIG group.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: A controlled trial of high-dose intravenous immune globulin infusions as treatment for dermatomyositis
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: The ProDERM trial was a double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that examined the effectiveness of IVIG for patients with dermatomyositis. Patients between the ages of 18 to 80 years with definite or probably active dermatomyositis were eligible for this study. Concomitant treatment with glucocorticoids and a maximum of two immunosuppressive drugs were allowed if the treatment was initiated at least three months prior, at a stable dose, and not exceeding the maximum allowable dose. Patients received either IVIG at a dose of 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight or a placebo (0.9% sodium chloride) every 4 weeks. TIS was the primary endpoint for a response, which is a weighted composite score reflecting changes in six measures of myositis activity over time. A total of 79% of patients in the IVIG group and 44% in the placebo group had at least minimal improvement defined as TIS>=20 at 16 weeks (95% confidence interval [CI], 16.7 to 53.2; p<0.001). In subgroup analyses, the percentage of patients who had a response in the IVIG group compared to placebo were the following: mild disease (73% vs. 27%), moderate disease (79% vs. 52%), and severe disease (86% vs. 50%). However, these analyses were underpowered to determine a difference in outcomes. A moderate response (TIS>=40) was observed in 68% of patients in the IVIG group and 23% in the placebo group. Additionally, a major improvement of TIS>=60 was seen in 32% and 8% respectively. At the end of the open-label extension phase, both the IVIG and placebo groups saw similar rates of minimum improvement (71% vs. 70%). A total of 113 IVIG-related adverse events were recorded, and five serious adverse events occurred after an IVIG infusion. No deaths and no hemolytic transfusion reactions were reported during the trial. In summary, IVIG shows promise as a therapeutic for dermatomyositis.
©2022 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.
2 Minute Medicine is the leading authoritative medical news licensing service, and the only with reports written by practicing doctors.

No ads & unlimited access to all current reports, over 9000 searchable archived reports, visual abstracts, Weekly Rewinds, and the online edition of The Classics Series™ textbook.
2 Minute Medicine® is an award winning, physician-run, expert medical media company. Our content is curated, written and edited by practicing health professionals who have clinical and scientific expertise in their field of reporting. Our editorial management team is comprised of highly-trained MD physicians. Join numerous brands, companies, and hospitals who trust our licensed content.
© 2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. - Physician-written medical news.

Join over 10 million yearly readers and numerous companies. For healthcare professionals
and the public.
Subscribe for free today!