#VisualAbstract: Lobar vs Sublobar Resection for Peripheral Stage IA NSCLC
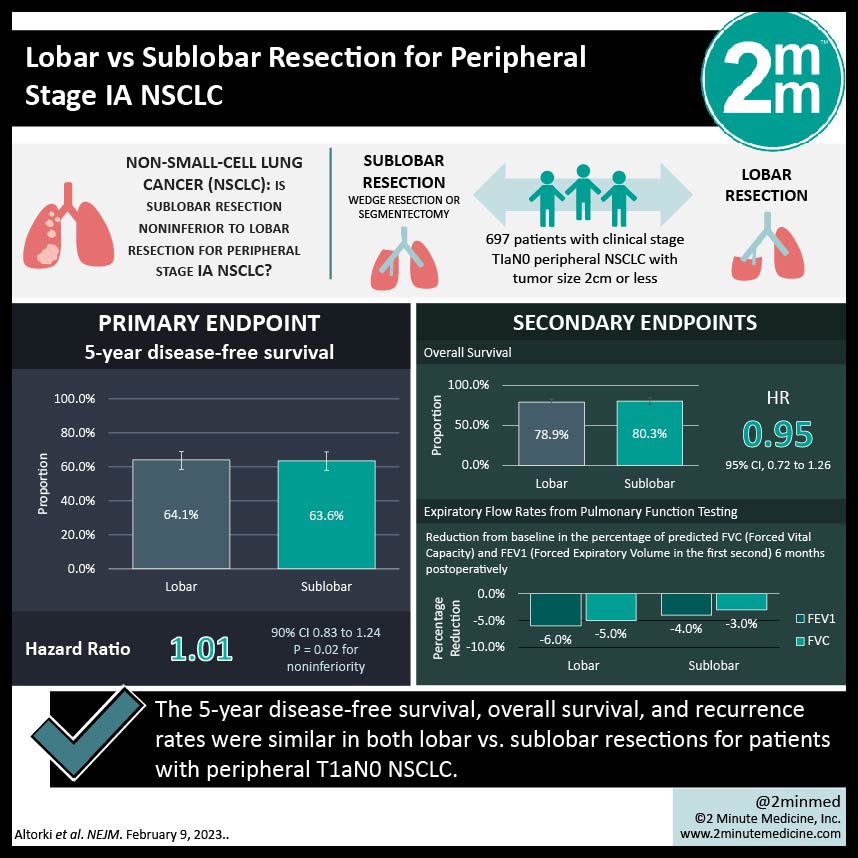
1. The 5-year disease-free survival, overall survival, and recurrence rates were similar in both lobar vs sublobar resections for patients with peripheral T1aN0 NSCLC.
2. Expiratory flow rates tested at 6 months postoperatively found that lobar resections had a greater reduction in FEV1 and FVC when compared to sublobar resection.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Historically, patients with T1N0 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were treated with lobectomy as opposed to sublobar resection based on previous research that showed worse outcomes with sublobar resection (increase in local recurrence and cancer-related mortality). Advances in imaging and staging methods since those initial studies, as well as new research showing the noninferiority of sublobar resection, have now reopened the debate. This study compared sublobar resection with lobectomy in patients with clinical stage IA NSCLC with tumour size 2cm or less. The primary endpoint was disease-free survival (DFS) and secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), local or systemic recurrence, and expiratory flow rates 6 months postoperatively. This study found similar 5-year DFS, OS, and recurrence rates in both groups; 63.6% in the sublobar resection group vs 64.1% in the lobar resection group with HR 1.01 for DFS, 80.3% vs 78.9% HR 0.95 for OS, and 70.2% vs 71.2% and an HR 1.05 for recurrence rate. Mean expiratory flow rates were tested at 6 months postoperatively. Both FEV1 and FVC were found to have a greater reduction in the lobar resection group (−6.0 and −5.0 respectively) vs the sublobar resection group (−4.0 and −3.0 respectively). The strengths of this study included the large sample size and the limitations of this study included strict inclusion criteria and only testing expiratory flow rates at one point in time. Overall, this study found that sublobar resection is non-inferior to lobar resection for patients with T1aN0 NSCLC.
Click to read the study in NEJM
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This randomized multicenter noninferiority phase 3 trial compared sublobar resection (wedge resection N=201, or segmentectomy N=129, total N=340) with lobectomy (N=357) in patients with clinical stage TIaN0 peripheral NSCLC with tumour size 2cm or less. The median follow-up was 7 years. The 5-year DFS was 63.6% (95%CI, 57.9 to 68.8) in the sublobar resection group vs 64.1% (95%CI, 58.5 to 69.0) in the lobar resection group, HR 1.01 (90%CI, 0.83 to 1.24). The 5-year OS was 80.3% (95%CI, 75.5 to 84.3) in the sublobar resection group vs 78.9% (95%CI, 74.1 to 82.9) in the lobectomy group, HR 0.95 (95%CI, 0.72 to 1.26). With the recurrence rates, the 5-year recurrence-free survival was 70.2% (95%CI, 64.6 to 75.1) in the sublobar resection group vs 71.2% (95%CI, 65.8 to 75.9) in the lobar resection group, HR 1.05 (95%CI, 0.80 to 1.39). It was reported that total deaths from lung cancer and other causes of death were similar across both groups. Expiratory flow rates were tested at 6 months postoperatively, and FEV1 was found to have a greater reduction in the lobar resection group (−6.0; 95%CI, −8.0 to −5.0) vs the sublobar resection group (−4.0; 95%CI, −5.0 to −2.0). Similarly, FVC was found to have a greater reduction in the lobar resection group (−5.0; 95%CI, −7.0 to −3.0) vs the sublobar resection group (−3.0; 95%CI, −4.0 to −1.0). Overall, this study found that sublobar resection is non-inferior to lobar resection for patients with T1aN0 disease.
©2023 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.