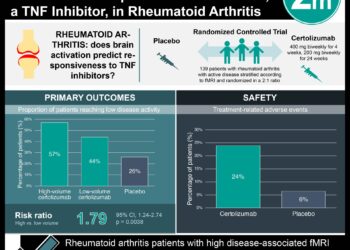
2 Minute Medicine Rewind May 21, 2018
Acupuncture is widely used by patients before and after undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies. Multiple early studies have indicated its benefits in terms of IVF outcomes; however, these studies have been characterized by a number of shortcomings, including small sample sizes and possible selection bias. In this single-blind, multicentre randomized controlled trial, 848 women undergoing a fresh IVF cycle were randomized to receive acupuncture (n=424) or a sham acupuncture control (n=424) to compare the efficacy of this intervention on live births. The first treatment was administered between days 6 to 8 of follicle stimulation, and 2 treatments were administered prior to and following embryo transfer. The sham control used a non-invasive needle placed away from the true acupuncture points. The primary outcome was defined as the delivery of 1 or more living infants at greater than 20 weeks’ gestation or birth weight of at least 400 grams. Researchers found that live births occurred among 74 women of 405 (18.3%) receiving acupuncture compared with 72 of 404 women (17.8%) receiving sham control (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.38). Researchers therefore concluded that there was no significant difference in live birth rates among women undergoing IVF with administration of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture at the time of ovarian stimulation and embryo transfer. Thus, the results of this study do not support the use of acupuncture to improve the success of IVF.
Migraine is a very prevalent disease, characterized by headaches that are severe and/or throbbing, accompanied by symptoms of photophobia, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes cognitive dysfunction. US guidelines recommend initiating preventive treatment in people who have at least 4 headache days per month, but approximately only 15% of those affected use preventative therapies. As such, there is a need for effective preventive therapy that targets the pathophysiology of migraine that is both safe and well tolerated. Fremanezumab, a fully humanized monoclonal antibody that targets calcitonin gene-related peptide, may be effective in the treatment of episodic migraine. In this randomized controlled trial, 875 patients with episodic migraine without previous treatment failure with 2 classes of migraine-preventive medication, were randomized 1:1:1 to receive subcutaneous monthly dosing of fremanezumab (225 mg at baseline, week 4, and week 8); a single higher dose of fremanezumab, as intended to support a quarterly dose regimen (675 mg of fremanezumab at baseline; placebo at weeks 4 and 8); or placebo (at baseline, week 4, and week 8) to assess the efficacy of fremanezumab for prevention of episodic migraine. The primary end point was the mean change in mean number of monthly migraine days during the 12-week period after the first dose. Researchers found that from baseline to 12 weeks, mean migraine days per month decreased from 8.9 days to 4.9 days in the fremanezumab monthly dosing group, from 9.2 days to 5.3 days in the fremanezumab single-higher-dose group, and from 9.1 days to 6.5 days in the placebo group. This resulted in a significant difference with monthly dosing versus placebo of -1.5 days (95% CI -2.01 to -0.93, p<0.001) and for the single higher dosing group versus placebo a difference of -1.3 days (95% CI -1.79 to -0.72, p<0.001). Researchers therefore concluded that fremanezumab significantly reduces the mean number of monthly migraines days when compared to placebo. Further studies are needed to compare this monoclonal antibody with other preventive medications, as well as determine the role of this medication in the management of refractory patients who have failed 2 or more classes of medications.
Association of Colonoscopy Adenoma Findings With Long-term Colorectal Cancer Incidence
Patients found to have adenomatous polyps are advised to undergo repeated colonoscopy surveillance to prevent subsequent colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the relationship between the adenomas at colonoscopy and long-term CRC incidence is unclear. Few studies have examined CRC incidence after adenoma removal. In this multicenter, prospective cohort study, 15,935 participants of the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer randomized clinical trial of flexible sigmoidoscopy (FSG) were followed up from 1993 with results to 2013 for CRC incidence. As part of the original randomized controlled trial, patients were randomized to FSG or usual care, with 15,935 patients going on to have colonoscopy. On initial colonoscopy, 18.1% of participants had an advanced adenoma, 31.8% had a non-advanced adenoma, and 50.1% had no adenoma. Patients with advanced adenoma were significantly more likely to develop CRC compared to patients with no adenoma (RR 2.7, 95% CI 1.9 to 3.7, p<0.001). Patients with advanced adenoma were also at significantly increased risk of death due to CRC (RR 2.6, 95% CI 1.2 to 5.7, p= 0.01) when compared to no adenomas. Risk of mortality in patients with non-advanced adenoma was not significantly increased compared to patients without adenomas. Thus, researchers concluded that patients with an advanced adenoma at diagnostic colonoscopy prompted by a positive FSG result were at significantly increased risk of developing CRC compared to those with no adenoma. The identification of a non-advanced adenoma may not be associated with increased CRC risk.
Effective diabetes self-management support has been shown to play an important role in addressing the long-term complications of poor diabetes control. The effectiveness of text messages (SMS) for diabetes self-management support programs (SMS4BG) is not known. In this 9-month, two arm, randomized controlled trial, 366 participants age 16 years and older with poorly controlled type 1 or type 2 diabetes (HbA1c ≥ 65 mmol/mol or 8%) were randomized to receive a tailored package of text messages for up to 9 months or usual care only to determine the effectiveness of SMS4BG. The text messages provided information, support, motivation, and reminders related to diabetes self-management and lifestyle behaviors. The primary outcome measure was change in glycemic control (HbA1c) from baseline to 9 months. Researchers found that the reduction in HbA1c at 9 months was significantly greater in the intervention group (mean -8.85 mmol/mol) compared to the control group (mean difference -4.23 mmol/mol, 95% Cl -7.30 mmol/mol to -1.15 mmol/mol, p= 0.007). Of the 21 secondary outcomes assessed, 4 showed statistically significant improvements in favor of the intervention group at 9 months, including foot care behavior, overall diabetes support, health status, and perceptions of illness identity. Researchers thus concluded that a tailored, text message-based, self-management support program may result in modest improvements in glycemic control in adults with poorly controlled diabetes. Further research into the use of SMS4BG and other text message-based support is required as part of improving self-management support and its accessibility.
Spontaneous, non-traumatic, intracerebral hemorrhage is the cause of up to 20% of all strokes, yet accounts for almost half of the deaths from all strokes worldwide. To date, only early intensive blood pressure lowering has been shown to improve functional outcomes after intracerebral hemorrhage. Tranexamic acid is routinely used for bleeding after trauma and post-partum hemorrhage. In this randomized controlled trial, 2325 adults with intracerebral hemorrhage were randomized to receive a 1 g IV tranexamic acid bolus followed by an 8 hour infusion of 1 g tranexamic acid, or a matching placebo within 8 hours of symptom onset to assess whether tranexamic acid reduces hematoma expansion and improves functional status at 90 days in adults with stroke due to intracerebral hemorrhage. Change in functional status was measured using the modified Rankin Scale. Researchers found that the primary outcome did not differ significantly between the groups (OR 0.88, 95% Cl 0.76 to 1.03, p=0.11). However, there were fewer deaths by day 7 in the tranexamic acid group versus the placebo group (OR 0.73, 95% Cl 0.53 to 0.99, p= 0.0406). There was no difference in case fatality at 90 days (HR 0.92, 95% Cl 0.77 to 1.10, p=0.37). Researchers therefore concluded that the administration of tranexamic acid does not significantly improve functional status or mortality at 90 days when compared to the current standard of care. Larger studies are needed to confirm or refute these findings in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage.
Image: PD
©2018 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.