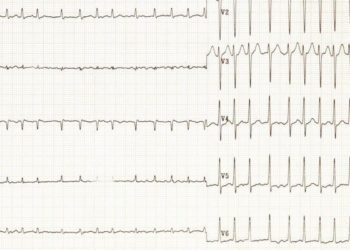
Atrial fibrillation likely increases risk of silent strokes
1. According to this systematic review, atrial fibrillation was linked to increased odds of silent cerebral infarctions, which are risk factors for future symptomatic strokes and dementia.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects nearly three million Americans and is known to predispose patients to strokes. However, it is unclear if AF also increases the risk for silent cerebral infarcts (SCI), in which small parts of the brain are deprived of oxygen without acute stroke symptoms. Because SCI may put patients at risk for future strokes and dementia, the authors conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the relationship between AF and SCI. Reviewing and analyzing studies that used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) to document the occurrence of SCI, the authors found that AF increased the odds of SCI between 2-3 fold. Unfortunately, because of limitations in available data, the relationship between anticoagulation—therapy routinely used for AF patients to prevent stroke—and SCI could not be determined. In addition, most of the included studies were cross-sectional, meaning that the annual risk of SCI could not be reliably calculated. Overall, the increased odds of SCI in AF patients may reflect an increased risk for cognitive impairment and future strokes, highlighting the need for more data on SCI to guide therapy for AF patients.
Click to read the study, published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Silent Brain Infarcts and the Risk of Dementia and Cognitive Decline
In-Depth [systematic review]: This systematic review analyzed the relationship between both paroxysmal and persistent AF and MRI and CT-diagnosed SCI among patients without clinical history of strokes or prosthetic valves. The authors reviewed 11 studies (5,317 patients) in this analysis, and after excluding autopsy studies due to heterogeneity and low sensitivity for detecting SCIs, 9 studies were included. MRI was more sensitive than CT in detecting SCI, although MRI-based studies used a more heterogeneous set of criteria to define SCI than did studies based on CT. Patients with AF had an increased odds of SCI by both MRI (OR 2.30; 95%CI 1.44-3.68), and CT (OR 3.45; 95%CI 2.03-5.87). In a sensitivity analysis, restricting odds calculations to patients with paroxysmal vs. persistent AF had little effect on odds of SCI. Due to lack of data on the relation between anticoagulation and SCI prevalence, further investigation into this relationship, and the possible inclusion of SCI in scores such as CHADS2, may be useful in deciding anticoagulation in AF patients.
More from this author: HIV rebound observed after therapeutic stem cell transplant USPSTF recommends behavioral counseling to reduce cardiovascular disease ACP recommends non-pharmacologic treatment of urinary incontinence in women Corticosteroids and physical therapy equally effective for shoulder impingement syndrome
Image: PD
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.