Benralizumab not shown to ameliorate COPD exacerbation rates when compared to placebo
1. Two complementary phase 3 clinical trials randomized patients with moderate-to-severe COPD to receive either benralizumab or a placebo and found that the trial agent did not lead to a significant reduction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation rates.
2. Safety outcomes were comparable between groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: COPD leads to progressive limitation to airflow into the lungs leading to worsening respiratory function. COPD is often also associated with eosinophilic inflammation which ultimately affects patients’ responsiveness to glucocorticoid medication. Benralizumab, an interlukin-5 receptor alpha-directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody, has been evaluated as an agent that leads to substantial eosinophil depletion which could ameliorate respiratory symptoms. In this analysis, complementary phase 3 studies GALATHEA (Benralizumab Efficacy in Moderate to Very Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with Exacerbation History) and TERRANOVA (Efficacy and Safety of Benralizumab in Moderate to Very Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with Exacerbation History) were conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of benralizumab versus placebo among patients with moderate to severe COPD. There was not a significant difference in COPD exacerbation rates among patients on benralizumab versus placebo. They also did not note any difference in serious adverse events between groups.
This study underscores that eosinophil depletion may not have an effect in ameliorating COPD exacerbations. It is notable that it included merging of results from two separate but related trials and limited by the depth of subgroup analysis reported.
Click to read the study in NEJM
Relevant Reading: Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for eosinophilic asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
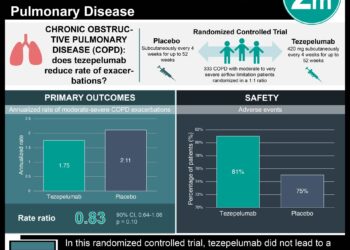
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: GALATHEA (n=1120) and TERRANOVA (n=1545) were both phase 3, double-blind, parallel-group randomized control trials. Eligible patients were randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio (GALATHEA) or 1:1:1:1 ratio (TERRANOVA) to either receive benralizumab or placebo via subcutaneous injection every four weeks. Doses of benralizumab were administered at either 30mg for asthma treatment or 100mg for the GALATHEA trial and at either 10mg, 30mg or 100 mg in the TERRANOVA trial. The primary endpoint of both trials were the treatment effects of benralizumab versus placebo, determined by the rate of COPD exacerbations after 56 weeks of treatment. Secondary endpoints included changes in FEV1, changes in the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) score, and occurrence of any adverse events. The annual COPD exacerbation rate in GALATHEA was noted to be 1.19 per year among patients receiving 30mg benralizumab (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 1.36) and 1.03 among patients randomized to receive 100mg benralizumab (95% CI, 0.90 to 1.19) versus 1.24 in the placebo group (95% CI, 1.08 to 1.42). The annual COPD exacerbation ratio in TERRANOVA was noted to be 0.99 in the 10-mg benralizumab group (95% CI, 0.87 to 1.13), 1.21 in the 30mg benralizumab group (95%CI, 1.08 to 1.37), 1.09 in the 100mg benralizumab group (95%CI, 0.96 to 1.23) and 1.17 in the placebo group (95% CI, 1.04 to 1.32). In the GALATHEA trial, the mean change from baseline in FEV1 was 7mL in the 30mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -35 to 48) and 21 ml in the 100mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -12 to 62). Changes in SGRQ scores were noted to be -1.011 in the 30mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -2.887 to 0.865) and -2.136 in the 100mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -4.020 to -0.251). In the TERRANOVA group the mean change from baseline in FEV1 was 15mL in the 10mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -29 to 59), -7mL in the 30mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -51 to 37) and 20mL in the 100mg benralizumab group (95% CI, -24 to 64). Differences in SGRQ scores were -1.011 (95% CI, -3.192 to 1.171) in the 10mg group, -1.388 in the 30mg group (95% CI, -3.562 to 0.786) and -0.602 in the 100mg group (95% CI, -2.763 to 1.560). In terms of safety events, both trials led to eosinophil depletion among patients who took benralizumab, however adverse events occurred at a similar rate in both trial and placebo groups.
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc