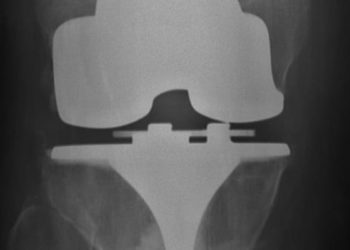
Bundled payment system for joint replacement may reduce costs
1. In this cross-sectional study conducted at a large health care system in San Antonio, TX, bundled payments for joint replacement procedures were associated with both hospital savings and reduced Medicare payments.
2. Decreases in post-acute care spending only occurred if it was included in the payment bundles.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Fair)
Study Rundown: Bundling payments for particular phases of health care is being evaluated as a way to reduce costs. This was studied for joint replacements and was shown to reduce costs. However, it is not clear which parts of the bundled payments are reducing costs for Medicare and hospitals. This observational study aimed to analyze changes in quality, internal hospital costs, and post-acute care (PAC) spending for lower extremity joint replacement bundled payment episodes encompassing hospitalization and 30 days of PAC.
Overall Medicare episode expenditures decreased for both joint replacements that were complicated and uncomplicated. Re-admissions and emergency department visits also decreased. However, patient illness severity remained stable. Over half of the hospital savings came from internal cost reductions (mostly due to reduction in implant costs per case) and just under half of the savings came from PAC spending reductions (both in inpatient rehabilitation and skilled nursing facility spending). Limitations of this study included using a single hospital system, observational nature of the study, and not evaluating the functional status of the patients afterwards (to determine if the changes in type of implant used affected patient outcomes).
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Medicare’s Bundled Payment initiative: most hospitals are focused on a few high-volume conditions
In-Depth [cross-sectional study]: This study followed 3942 patients who received a lower extremity joint replacement from approximately 800 hospitals in the Baptist Health System that participated in Medicare’s Acute Care Episode and Bundled Payments for Care Improvement demonstration projects. The main observational outcomes of interest included average Medicare payments per episode, re-admissions, emergency department visits, prolonged length of stay, and hospital savings from changes in hospital and PAC spending. Descriptive statistics and scatterplots were used to analyze trends in spending.
Between 2009 and 2015 there were 3942 joint replacements where patient demographics and severity of illness did not change significantly. Average Medicare episode payments for both complicated and non-complicated lower extremity joint replacements declined significantly during the bundled payment episode period. There were also significant decreases in hospital costs over this time period: 51.2% from internal cost reductions like using less costly implants (29% cost reduction per case) and 48.4% from PAC spending reductions (27% cost reduction per case). This was largely due to reductions in inpatient rehabilitation and skilled nursing facility spending.
Image: CC/Wiki
©2016 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.