Chlorhexidine may not benefit intubated non-cardiac surgery patients
Image: PD
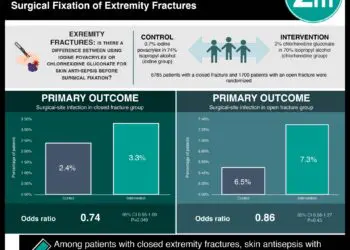
1. A significant decrease in lower respiratory tract infections was noted in cardiac-surgery patients with the use of chlorhexidine.
2. Although there was no decrease in mortality noted with the use of chlorhexidine in cardiac-surgery or non-cardiac surgery studies, there was a non-significant increase in mortality in the non-cardiac surgery studies.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
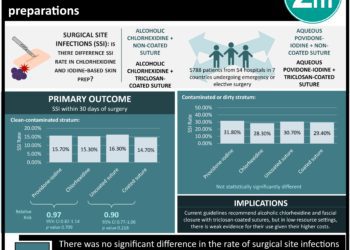
Study Rundown: Oral care including the use of chlorhexidine gluconate in mechanically ventilated patients has become the standard of care. The authors of this study feel that the evidence supporting this practice might not be as robust as expected, as these recommendations are based on meta-analyses that do not distinguish between cardiac and non-cardiac patients and combine open-label and double-blind trials. After stratifying the trials in such categories, the authors found that although there was no significant decrease in ventilator-associated pneumonia in non-cardiac surgery patients, there was a decrease in lower respiratory tract infections in cardiac surgery patients. In addition, there were no significant reductions in either group in the mean duration of mechanical ventilation. Mortality differences were also not seen in either group; however, there was a non-significant increase in mortality in the non-cardiac surgery studies. Strengths of the study include the strategy of stratification of studies into cardiac, non-cardiac, open-label, and double-blinded categories. However, as this is a meta-analysis of several trials with different methodologies and their own limitations, a better randomized double-blinded placebo controlled trial addressing the concerns raised in this paper should be undertaken prior to changing standard practices.
Click to read the study in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: Oral decontamination for prevention of pneumonia in mechanically ventilated adults: systematic review and meta-analysis
In-Depth [systematic review and meta-analysis]: The authors of this study examined PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and CINAHL, without date or language restrictions. Randomized clinical trials comparing chlorhexidine to placebo in intubated adults were included. Of 171 citations, 16 trials met inclusion criteria and were then stratified according to cardiac vs. non-cardiac surgery and open-label vs. double-blind investigations. No significant difference was seen in the non-cardiac surgery group for the outcome of ventilator-associated pneumonia (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.66-1.16). Significant reductions in lower respiratory tract infections were noted in the cardiac-surgery patients randomized to Chlorhexidine (RR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.41-0.77). Also, there was no significant mortality difference in the cardiac surgery studies (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.25-2.14) but there was a non-significant trend towards increased mortality in the non-cardiac surgery studies (RR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.99-1.29).
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.