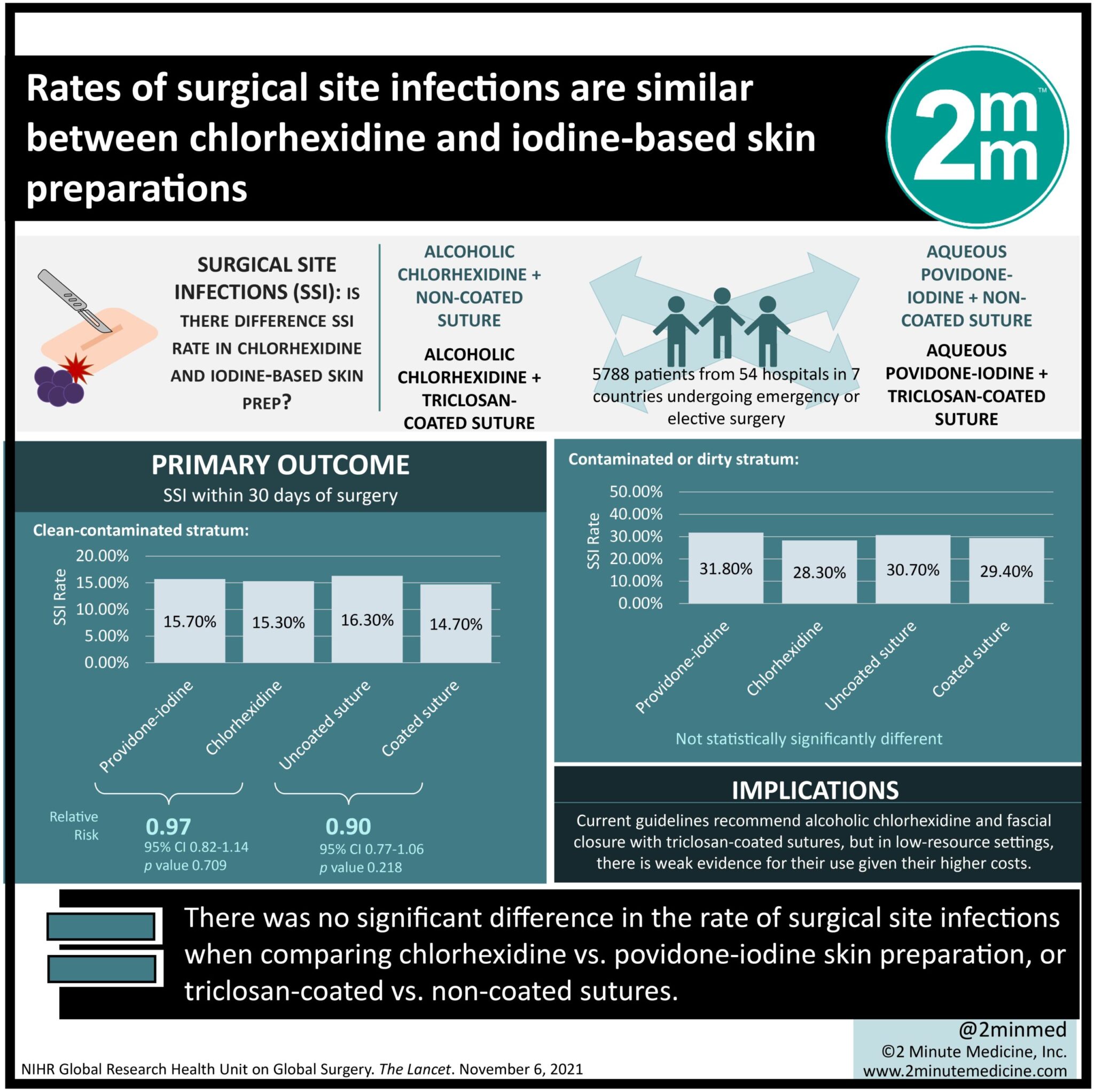
#VisualAbstract: Rates of surgical site infections are similar between chlorhexidine and iodine-based skin preparations
1. There was no significant difference in the rate of surgical site infections when comparing chlorhexidine vs. povidone-iodine skin preparation, or triclosan-coated vs. non-coated sutures.
2. In low-resource settings, there is weak evidence for use of alcoholic chlorhexidine and triclosan-coated sutures, given their comparable efficacy but higher costs.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Surgical site infections (SSI) are a common postoperative complication that causes patients a significant health burden due to pain, poor wound healing, and prolonged recovery time. Patients in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are particularly affected by SSI. Current guidelines recommend the use of alcoholic chlorhexidine and fascial closure with triclosan-coated sutures; although, there is insufficient evidence for their use in low-resource settings. This randomized controlled trial aimed to study both interventions in LMICs with povidone-iodine skin preparation and non-coated sutures as the respective controls. The primary outcome was SSI within 30 days of surgery, while key secondary outcomes included SSI at discharge and postoperative mortality. According to study results, there was no difference in the rate of SSI with alcoholic chlorhexidine versus povidone-iodine or with triclosan-coated sutures versus non-coated sutures. This study was strengthened by a large sample size, a 2×2 factorial design and randomization of participants into one of four groups.
Click to read the study in The Lancet
Relevant Reading: Health and Economic Outcomes Associated With COVID-19 in Women at High Risk of HIV Infection in Rural Kenya
In-depth [randomized controlled trial]: Between Dec 10, 2018, and Sept 7, 2020, 5788 patients were assessed for eligibility from 54 hospitals in seven countries. The inclusion criteria were broad and included all patients undergoing emergency or elective surgery. Individuals with an allergy to chlorhexidine skin preparation solution were excluded. The 3091 patients in clean-contaminated stratum and 2697 patients in contaminated or dirty stratum were randomized into one of four groups: 1446 to alcoholic chlorhexidine and non-coated suture, 1446 to alcoholic chlorhexidine and triclosan-coated suture, 1447 to aqueous povidone-iodine and non-coated suture, and 1449 to aqueous povidone-iodine and triclosan-coated suture.
The primary outcome of SSI within 30 days of surgery was similar for alcoholic chlorhexidine versus povidone-iodine (clean-contaminated stratum: 15.3% vs. 15.7%, relative risk [RR] 0.97; contaminated or dirty stratum: 28.3% vs. 31.8%, RR 0.91) and triclosan-coated sutures vs. non-coated sutures (clean contaminated stratum: 14.7% vs. 16.3%, RR 0.90; contaminated or dirty stratum: 29.4% vs. 30.7%, RR 0.98). Findings from this study do not suggest the routine use of 2% alcoholic chlorhexidine and triclosan-coated sutures in low-income settings to prevent SSI.
©2021 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.