Combined patient and provider intervention associated with improvement in osteoarthritis management in veterans
1. From a randomized clinical trial, intervention at both the patient and provider level showed modest improvement in osteoarthritis management of patient function and physical activity when compared to control subjects.
2. Depressive symptoms, BMI, and pain scores of patients were not significantly affected by interventional methods.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Osteoarthritis is an increasingly prevalent cause of chronic illness, pain, and disability. While evidence-based guidelines indicate the importance of clinical strategies and behavioral changes in improving osteoarthritis outcomes, many clinical strategies are underused and a large proportion of patients are physically inactive or overweight. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of combined patient and provider intervention in improving osteoarthritis management and improving overall patient outcomes. This study involved veterans enrolled in the Durham Veteran Association (VA) Medical Center and 30 of the center’s primary care providers. The patient’s primary outcome was assessed using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC). Notably, a moderate improvement in total WOMAC scores was observed in the osteoarthritis intervention group, while the control group remained around baseline levels. Clinically meaningful improvements in WOMAC scores have typically ranged from 12% to 18%, rather than the 8.5% observed in this trial. However, due to the design of this trial, it is not possible to determine the individual effects of patient and provider intervention, thereby limiting the analysis of the efficacy of these measures. Additionally, there may be limited generalizability of the study, as the patients receiving care at the VA medical center were mostly male. However, this study provides evidence that patient and provider intervention may improve the management of osteoarthritis.
Click to read the study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine
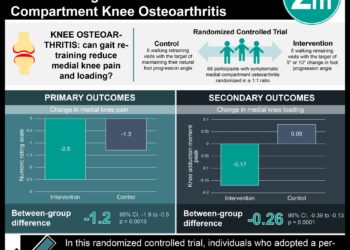
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: The trial identified patients with hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, or both, in addition to patients that were overweight (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2), not adhering to physical activity recommendations (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services), and reported joint symptoms. Participants then were randomly assigned to either the control (i.e., patients received their usual care) or osteoarthritis intervention group. Patient intervention involved telephone calls aimed at improving patient physical activity, weight management, and goal setting over the course of 12 months, while provider intervention included patient-specific osteoarthritis treatment recommendations according to a developed algorithm based on published treatment guidelines. At the conclusion of the study, the estimated mean change in total WOMAC score was –4.0 points (95%CI –6.2 to –1.8 points) in the osteoarthritis intervention group and 0.1 points (95%CI –2.3 to 2.3 points) in the control group. Furthermore, the estimated mean difference between groups was –4.1 (95%CI –7.2 to –1.1 points, p = 0.009). In secondary outcome analysis, no significant differences were observed between groups for BMI, WOMAC pain subscale score, or depressive symptoms; however, improvements were observed in changes to exercise from baseline physical activity and WOMAC function subscale score.
Image: CC/Wiki
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.