Comparison of GFR estimation methods in older adults
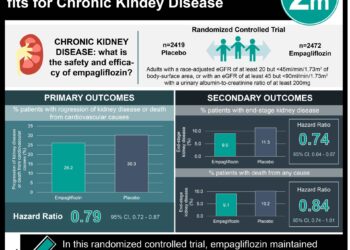
1. In this cross sectional study of older adults (>65 years) who had undergone gold-standard glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measurement with inulin excretion, different methods of estimating GFR demonstrated variation in bias and accuracy.
2. Despite the observed differences in bias and accuracy in this study population, differences were not clinically relevant with no one method demonstrating superior diagnostic performance.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
Study Rundown: Renal function deteriorates with age, and renal insufficiency is estimated to affect up to 47% of US adults over the age of 70 years. Accurate measurements of renal function are important in order to recognize patients at risk for consequences of renal disease and to accurately dose medications that rely on renal function. Gold-standard measurement of GFR with clearance of inulin, iohexol, or other reference methods are not feasibly done in most patients. Methods to calculate estimated GFR (eGFR) are available but their performance in older patients and across a range of GFR have been questioned. The current study used a cross-section of older adults who had undergone inulin excretion GFR measurement and evaluated the performance of four different methods of eGFR calculation based on bias and accuracy. The four methods of calculation included the following: Chronic Kidney Disease – Epidemiology Collaboration, Lund-Malmo Revised, Full Age Spectrum, Berlin Initiative Study. Though small differences in diagnostic performance were observed there was no clinically meaningful difference between the four methods.
The main strength of this study was the large number of older adults across a range of GFR values for whom inulin excretion measurements were performed. The limitations of this study include the lack of data on ethnicity, the single institution data source, lack of data on cystatin C which can improve interpretation of GFR when using creatinine, and relatively few patients with more severe renal impairment (GFR <30 mL/min/1.73m2).
Click to read the study in JAMA Internal Medicine
Relevant Reading: GFR estimation based on standardized creatinine and cystatin C: a European multicenter analysis in older adults
In-Depth [cross-sectional study]: This study is a retrospective cross-sectional study that included adults aged 65 to 90 years who underwent inulin excretion GFR measurement for suspected or established renal dysfunction, before kidney donation, or after kidney transplant between 2003 and 2017. Measurements were excluded if they were using the iohexol method, or were repeated measurements as only the first value was included for any patient. The study evaluated bias, precision, and accuracy for plasma-creatinine-based equations Chronic Kidney Disease–Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI), Lund-Malmö Revised, (LMR), full age spectrum (FAS), and Berlin Initiative Study (BIS) 1.
The study included 2247 participants with a median (SD) age of 71.5 (5) years. There were differences in median bias between CKD-EPI vs LMR (−4.0 [–4.0 to –3.5 mL/min/1.73m2; P < .001]) and CKD-EPI vs FAS (–2.0 [–3.5 to –2.5] mL/min/1.73m2, P < .001) but not significant between CKD-EPI vs BIS 1 (0.0 [–1.5 to 0.5], P = .07, Mood test). In patients aged 65 to 74 years with measured GFR<45 mL/min/1.73m2, the difference in median P30 (95%CI) was significant vs BIS 1 (P = .004, McNemar test). In subjects 75 years and older, with measured GFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73m2, LMR and BIS 1 were more accurate than CKD-EPI and FAS (P30 = 74.5 [70.0-79.5] and 73.0 [68.0-78.0] vs 69.0 [64.5-74.0] and 69.0 [65.5-72.0]).
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.