CPAP found equal to intubation in extremely premature infants in the NICU
[tabs tab1=”2MM Rundown” tab2=”Full 2MM Report”]
[tab]
Image: PD
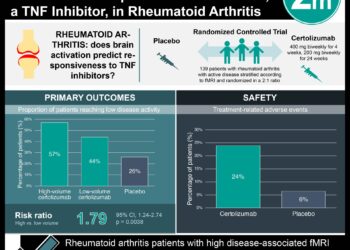
1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) may be a viable alternative to early intubation with surfactant administration in extremely preterm infants in the NICU.
2. There is a higher mortality rate in extremely preterm infants when a low target oxygen saturation (85 to 89%) is used.
This study compared different methods of oxygenation in extremely preterm infants in the NICU. Authors found that noninvasive CPAP could be used as an alternative to early intubation with surfactant administration. However, since lower oxygenation groups had a higher rate of mortality, higher oxygenation saturation targets are recommended for infants who are extremely preterm.
The strengths of this study are the large sample size and the high follow up rate. The limitations of this study are that the results are based only upon a single visit and that disabilities may not be unearthed until later childhood.
Click to read the study in NEJM
[/tab]
[tab]
Image: PD
1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) can be used as an alternative to early intubation with surfactant administration in extremely preterm infants in the NICU.
2. There is a higher mortality rate in extremely preterm infants when a low target oxygen saturation (85 to 89%) is used.
Primer: With improvements in ventilation and creation of exogenous surfactants, infants born at 24 weeks of age can survive in the neonatal intensive care units (NICU). However, these extremely premature infants are at higher risk of death and developing neurological disorders such as intellectual delay, blindness, and cerebral palsy. Although lifesaving, early intubation with surfactant administration can lead to bronchopulmonary dysplasia due to mechanical scarring and high oxygen radicals. The purpose of the SUPPORT Trial was to compare the use of non-invasive continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) on extremely premature infants to intubation with surfactant administration. Infants at 36 weeks showed no differences in the rates of death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The results at the corrected age of 18 to 22 months are reported in this study.
Background reading:
- Neurologic and developmental disability after extremely preterm birth.
- Early CPAP versus surfactant in extremely preterm infants.
This [double blind, randomized control] study compared the use of CPAP to early intubation with surfactant administration with high and low oxygen saturation (85-89% vs. 91 to 95%) in 1316 extremely preterm infants, after 18 to 22 months.
Overall mortality did not differ between the CPAP and surfactant group. However, the lower oxygenation group had a significantly higher mortality rate than the higher oxygenation group. Furthermore, infants in the lower gestational-age stratum had a higher mortality in the surfactant group compared to the CPAP group. There were also no differences in the frequency of neurological development between any of the groups.
In sum: This study compared different methods of oxygenation in extremely preterm infants in the NICU. They found that noninvasive CPAP could be used as an alternative to early intubation with surfactant administration. However, since lower oxygenation groups had a higher rate of mortality, higher oxygenation saturation targets are recommended for infants who are extremely preterm.
The strengths of this study are the large sample size and the high follow up rate. The limitations of this study are that the results are based only upon a single visit and that disabilities may not be unearthed until later childhood.
Click to read the study in NEJM
By [JC] and [MS]
© 2012 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT. Content is produced in accordance with fair use copyrights solely and strictly for the purpose of teaching, news and criticism. No benefit, monetary or otherwise, is realized by any participants or the owner of this domain.
[/tab]
[/tabs]