CT-based assessment may predict the need for open heart surgery
1. Among a cohort of patients with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD), coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) was comparable to invasive coronary angiography in evaluating candidacy for coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
2. The combination of CCTA with a CCTA-based CAD grading scale showed significantly higher specificity and positive predictive value than CCTA alone for predicting CABG candidacy.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
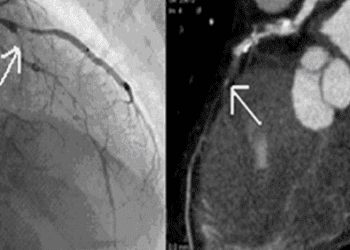
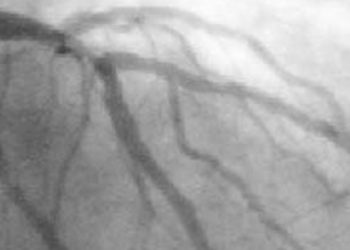
Study Rundown: Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) provides a noninvasive method for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) and can potentially aid in the management and risk stratification of patients with CAD. Little research exists, however, to support the use of CCTA for evaluating patients with CAD for a potential percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and/or identifying patients who may benefit from CABG. For these treatment-level decisions, invasive cardiac angiography (ICA) currently exists as the gold standard. The SYNTAX score, derived from ICA data, helps stratify patients with CAD who may benefit from CABG and/or PCI. In this study, researchers sought to evaluate the performance of a CCTA and a CCTA-derived SYNTAX score as strategies for non-invasively identifying CABG surgery candidates based current guidelines.
The results of the study suggested that CCTA alone is highly sensitive and specific for the identification of patients that would benefit from CABG surgery. Additionally, the combination of CCTA with a CCTA-derived SYNTAX score was able to identify CABG surgery candidates with a higher specificity and positive predictive value than CCTA alone when compared to the ICA-based SYNTAX score reference. This study suggests that it may be possible to non-invasively identify patients with CAD who may be benefit from surgery, providing more time to patients and provider to evaluate the next step in management. This study was limited in its study design, and future studies should evaluate the ability of CCTA and CCTA-based SYNTAX scores to prospectively identify patients for CABG when compared with ICA. Also, although this study was able to identify candidates for CABG, it had limited ability in predicting those who actually did undergo surgery. This is partially due to the fact that the decision to undergo surgery is influenced by more than just the severity of CAD, and future evaluations may hope to incorporate these other influencing factors to create a more composite predictor of the need for surgery.
Click here to read the study in Radiology
Relevant reading: The SYNTAX score and its clinical implications
In-depth [retrospective cohort]: In this study, medical records from 399 patients who had undergone both CCTA and ICA over a six-month period in 2010 were reviewed, and their need for PCI, CABG, and/or medical treatment were recorded. The study population included 244 men and 155 women with an average age of 63.8 years. SYNTAX scores were evaluated based on ICA and CCTA, and compared retrospectively by two experienced readers. Patient criteria for CABG surgery were taken from the 2011 American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association practice guidelines. For these patients, CCTA alone had an overall sensitivity of 96.5%, specificity of 96.5%, positive predictive value 88.3%, and negative predictive value of 99% for evaluating CABG surgery candidates. The combination of a CCTA-based SYNTAX score and CCTA was able increase the specificity (98.3%) and positive predictive value (86%) (P<.0001). Patients that met CCTA CABG criteria were, on average, older and had a greater CAD burden. Of those patients that met surgical criteria, 23 (24.5%) underwent CABG in the CCTA group versus 22 (25.6%) in the ICA group.
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.