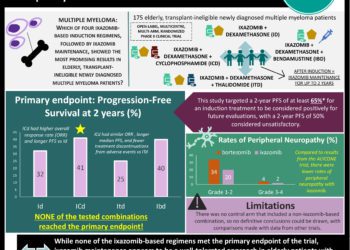
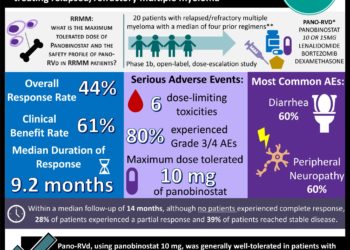
Diffusion tensor imaging valuable in the evaluation of peripheral neuropathy
Image: CC/Schultz
1. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was shown to be both sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy among asymptomatic patients with electromyographic (EMG) evidence of nerve injury.
2. Utilization of DTI was shown to be superior to the current imaging standard for peripheral neuropathy, magnetic resonance (MR) neurography.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
Study Rundown: MR neurography is an established technique for the evaluation of known or suspected peripheral neuropathy, and is associated with a high diagnostic accuracy. DTI, a newer MR-based imaging technique, has shown promise in the early detection of a number of neurologic conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease, and previous work has suggested a role for DTI in the evaluation of peripheral nerve disease. The current study evaluated the utility of DTI in the evaluation of patients with asymptomatic peripheral neuropathy of the ulnar nerve, with EMG evidence of nerve injury as the diagnostic reference standard. Results of the investigation suggested superior diagnostic performance of DTI relative to standard MR neurography, with both quantitative and qualitative improvements in the detection of subtle nerve injury. The primary limitation of the study was sample size. Further work is necessary to replicate these findings in a larger patient cohort, in different neuropathic conditions, and in patients with symptomatic disease.
Click to read the study in Radiology
Relevant Reading: Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain
In-Depth [prospective cohort]: This study included 30 participants without symptoms of peripheral ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. To assess for subclinical nerve injury, all participants received EMG of the ulnar nerve. Evidence of peripheral ulnar neuropathy was defined as decreased nerve conduction velocity (NCV) within the distribution of the ulnar nerve at the retroepicondylar groove. Participants also underwent diffusion tensor imaging in addition to standard, T2-weighted MR neurography. T2 signal intensity and the DTI metric fractional anisoptropy (FA) were quantitatively derived from the relevant portion of the ulnar nerve to assess for surrogate evidence of nerve injury, and mean values were compared between groups. Correlation between imaging abnormalities and the magnitude of nerve injury by EMG were determined using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Both FA and T2 intensity were also qualitatively assessed through visual inspection of color FA maps and T2-weighted MR images.
A total of 10 patients (33%) were identified as having ulnar neuropathy on EMG, while 20 patients (66%) had no evidence of EMG abnormality (controls). As compared to the control patients, T2 signal intensity was significantly increased across the retroepicondylar groove among patients with EMG-demonstrated peripheral ulnar neuropathy (76.2 msec ± 13.7 vs 64.2 msec ± 10.9; p = .01), while FA was significantly decreased (0.41 ± 0.07 vs 0.51 ± 0.09; p = .006). Despite this, mean FA values significantly correlated with absolute NCVs (r = 0.51, p = .005), while average T2 signal intensities did not. Qualitative, blinded review of color FA maps yielded a sensitivity and specificity for FA of 83% and 80%, respectively, for the diagnosis of peripheral ulnar neuropathy. A similar blinded review of T2-weighted images yielded a sensitivity and specificity of 55% and 63%, respectively. Taken in aggregate, these data suggest an improved diagnostic performance for DTI in the evaluation of mild peripheral neuropathy relative to standard T2-weighted MR neurography.
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.