Fibrinolysis for pulmonary embolism may prevent hemodynamic collapse [PEITHO trial]
Image: CC/Heilman
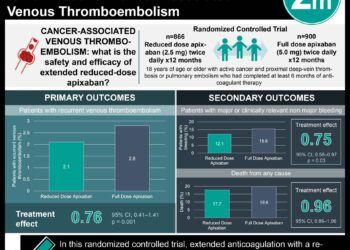
1. Fibrinolysis in addition to standard anticoagulation reduced hemodynamic decompensation, but did not affect overall mortality, in patients with intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism.
2. Fibrinolysis was associated with greater risk of bleeding and stroke.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
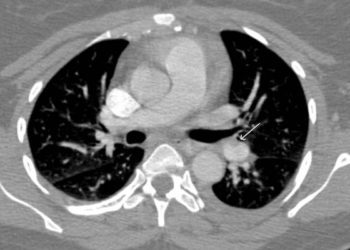
Study Rundown: A pulmonary embolism (PE) that causes persistent hypotension is considered a massive PE. Those that do not meet this criterion are considered submassive. At present, fibrinolytic therapy is only indicated for massive PE. This trial investigates whether fibrinolytic therapy is appropriate for cases of submassive PE where there is evidence of right ventricular dysfunction and myocardial injury – what the authors call intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Fibrinolysis in this setting has been a controversial subject and this is the largest trial to address this question thus far.
The primary outcome in this trial was a composite of hemodynamic decompensation and death from any cause within 7 days of randomization. The results show that fibrinolysis in addition to standard anticoagulation reduced the primary outcome by about 50%. However, fibrinolysis primarily reduced the incidence of hemodynamic decompensation. There was no difference in overall mortality between the two groups either at 7 or 30 days. Death was an infrequent event in both groups, suggesting that the placebo group strategy of standard anticoagulation followed by fibrinolysis in the event of hemodynamic collapse could be a valid approach to management of these patients. Fibrinolysis was associated with a significant increase in the incidence of major extracranial bleeding and stroke.
Click to read the study, published today in NEJM
Click to read the accompanying editorial in the NEJM
Relevant Reading: Prognostic value of right ventricular dysfunction in patients with haemodynamically stable pulmonary embolism: a systematic review
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: A total of 1006 patients from multiple countries were randomized to standard anticoagulation with heparin plus a one-time bolus of either the fibrinolytic, tenecteplase or a bolus of placebo. These were patients with intermediate-risk PE based on CT and/or echocardiography findings consistent with right ventricular dysfunction, plus evidence of myocardial injury confirmed by increased troponin levels.
The primary composite outcome of hemodynamic deterioration or death within 7 days was significantly lower in the fibrinolysis group (2.6% vs. 5.6%, P=0.02). Death within 7 days was not significantly different between the two groups (1.2% vs. 1.8%, P=0.42). There was a lower incidence of hemodynamic decompensation in the fibrinolysis group (1.6% vs. 5.0%, P=0.002).
There was a significantly higher incidence of bleeding and stroke in the fibrinolysis group in the first 7 days: major extracranial bleeding (6.3% vs. 1.2%, P<0.001); minor bleeding (32.6% vs. 8.6%); major bleeding (11.5% vs. 2.4%); stroke (2.4% vs. 0.2%, P=0.003). There was a similar incidence of serious adverse events within the first 30 days after randomization (10.9% vs. 11.8%, P=0.63).
More from this author: Early risk factor for progression of cystic fibrosis identified, Gut microbes implicated in stroke and heart attacks: new dietary link, New leukemia mutation offers therapeutic targets, Childhood ADHD associated with increased risk of suicide, A marker of aggressive liver cancer and potential therapeutic target identified
©2012-2014 2minutemedicine.com. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2minutemedicine.com. Disclaimer: We present factual information directly from peer reviewed medical journals. No post should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2minutemedicine.com. PLEASE SEE A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IN YOUR AREA IF YOU SEEK MEDICAL ADVICE OF ANY SORT.