Large study describes characteristics of children with COVID-19 in China
1. Children of all ages were susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, with infants and younger children being most at risk for severe and critical illness. There was only 1 death reported.
2. Across all age groups, 94% of children had asymptomatic, mild, or moderate illness. 5% had severe illness, and <1% were critically ill.
Evidence Rating Level: 4 (Below Average)
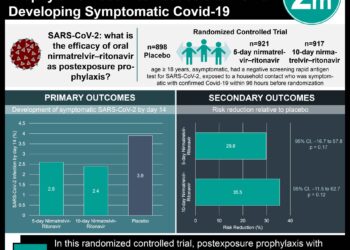
Study Rundown: Since the emergence of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection, in early December, little is known about outcomes in infected children. This large scale retrospective epidemiologic study examined characteristics and transmission patterns of 2143 children less than age 18 with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in China. Severity of illness in different age groups, time from illness onset to diagnosis, and transmission dynamics were reported. Median time from illness onset to diagnosis was 2 days. Severe and critical illness in children was seen far less commonly (5.9%) than that which has been reported in adult patients (18.5%). The largest proportion of severe and critical cases were seen in infants <1 year and children aged 1-5 years. Disease burden among children increased most rapidly in the early stage of the epidemic, spreading from Wuhan to surrounding areas and peaking at the beginning of February. Cases then declined steadily over time. One limitation of this study was the large number of suspected cases (65.9%) compared to laboratory confirmed cases (34.1%), with more severe infections occurring in the suspected cases. As an accompanying editorial points out, severe disease in children without virologic confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 infection may have been caused by other pathogens. Additionally, detailed clinical information and exposure history were not available for every patient and therefore clinical characteristics (including underlying medical conditions) and incubation periods were not assessed. Nonetheless, the study shows that while children with COVID-19 are less severely affected than adults, differences in illness severity exist between age groups, with younger children being most at risk for severe illness.
Click to read the study in Pediatrics
Click to read an accompanying editorial in Pediatrics
Relevant Reading: SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children (NEJM 3/18/2020)
In-Depth [case series]: This retrospective case series analyzed children less than 18 years of age with COVID-19 in China. Data was obtained from the China CDC electronic database. Both laboratory confirmed and clinically suspected cases were included in the analysis. Subjects were deemed to be suspected cases if they were at high risk of infection (exposed to a known COVID-19 case) and had 2 of the following: (a) fever, respiratory symptoms, gastrointestinal symptoms, or fatigue (b) normal white blood cell count, lymphopenia, or elevated C-reactive protein (c) abnormal chest X-ray. Children at lower risk of infection (no exposure to known case) were also included in the suspected case group if they met the above criteria and other respiratory infections were ruled out. Overall, 731 laboratory-confirmed cases and 1412 suspected cases were included. Illness severity was assessed in 5 age groups: <1, 1-5, 6-10, 11-15, and >15 years of age. Illness was considered to be severe if hypoxemia was present (SpO2 < 92%) and critical illness was defined as having acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or multisystem organ dysfunction. Results indicated that 10.6% of affected infants less than 1 year of age and 7.3% of children aged 1-5 years experienced severe or critical illness; children in those age groups were more likely to be severely or critically ill compared to children aged 6-10 (4.2%), 11-15 (4.1%), and > 15 years (3%). Across all ages, 5.9% were severely or critically ill and 55% of children were mildly ill or asymptomatic. One death occurred in a 14-year-old boy. Several explanations as to why children overall experience milder illness than adults were offered by study authors: Firstly, children may have stayed at home more frequently and had less exposure to infected individuals. Additionally, the suspected cellular receptor for SARS-CoV-2 viral binding (ACE-2) may be less mature and/or functional in children, leading to decreased ability of the virus to bind to cells and subsequently infect them. Finally, children may have increased levels of viral antibodies due to frequent exposures to other respiratory viruses, which may strengthen their ability to fight off SARS-CoV-2.
Image: PD
©2020 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.