Mindfulness-based therapy associated with improvement in quality of life for PTSD patients
1. In this study, mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) therapy resulted in a greater reduction in self-reported post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms and improved quality of life compared to present-centered therapy (PCT).
2. There was no significant difference in PTSD diagnosis status after treatment or at 2-month follow-up between the two groups.
Evidence Rating Level: 1(Excellent)
Study Rundown: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is triggered by life-threating events, with subsequent symptoms including nightmares, intrusive memories, emotional distress, feelings of numbness, and hopelessness, among others. Individuals with PTSD are at a greater risk of suicide, depression, and substance use disorders. Current treatment options for PTSD include cognitive therapy, exposure therapy, antidepressants, and anti-anxiety medications. Two additional options for treatment are mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and present-centered therapy (PCT). While the former option teaches meditation practices to the individual, the latter emphasizes the individual’s existing strengths in order to cope with stressors. The authors of this study compared these two methods as treatment options for PTSD in a randomized controlled trial.
The authors of this study found that MBSR resulted in a greater reduction in self-reported PTSD symptoms at 2-month follow-up as well as an improved quality of life when compared to PCT. There was no significant difference however in the rates of self-reported depressive symptoms or PTSD diagnosis status observed between the two groups. While this study was strengthened by its randomized controlled trial design, it was limited by the short follow-up period of 2 months, restricting our understanding of either treatment’s long-term effects. Due to inherent differences in the amount of contact required for either type of treatment (2.5 hour group sessions for MBSR and 1.5 hour group sessions for PCT), individuals in the active arm of this study received more clinician interaction than those in the control arm, potentially confounding results. Nevertheless, treatments such as MBSR may expand the therapeutic options available for PTSD. Future studies in this area should focus on further validation of such alternative PTSD treatments, particularly through long-term follow-up studies.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Click to read the accompanying editorial in JAMA
Relevant Reading: Meditation programs for psychological stress and well-being
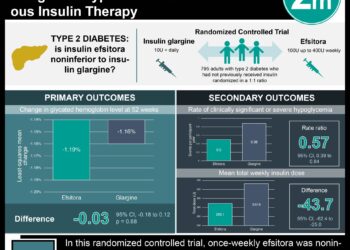
In-Depth [randomized controlled trial]: This study evaluated 116 veterans with PTSD from the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center between March 2012 and December 2013. Inclusion criteria were that veterans met a diagnosis of full or subthreshold PTSD per DSM-IV criteria, participated in no other PTSD psychotherapy during the study period, and received either no medications or were on a stable medication regimen. MBSR resulted in a greater reduction in self-reported PTSD symptoms according to the PTSD checklist at post-treatment and at 2-month follow-up from scores of 63.6 to 55.7 and then 54.4 vs. PCT, from 58.8 to 55.8 and then 56.0 (p = 0.002 and p 0<0.001, respectively). MBSR participants reported greater improvement in quality of life from baseline to 2-month follow-up than did those in PCT (mean score improvement MBSR from 75.6 to 80.2 vs. PCT from 76.4 to 75.8; mean difference in improvement 5.22, 95%CI 1.73-8.71). Differences between the two groups for change in PTSD diagnosis status after treatment and at 2 months follow-up between the two groups were not significant (42.3% and 53.3% loss of diagnosis of PTSD with MBSR, respectively; and 43.9% and 47.3% loss of diagnosis of PTSD with PCT, respectively).
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.