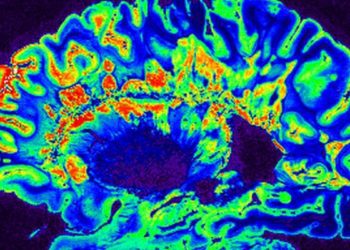
Targeted MRI may improve sensitivity for multiple sclerosis diagnosis
1. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging performed with a myeloperoxidase (MPO)-specific contrast agent was more sensitive for the detection of preclinical and subclinical disease activity than conventional MR imaging in a murine model of multiple sclerosis.
2. By quantifying MPO activity, the gadolinium-based MPO imaging technique identified more lesions than the standard detection method at remission and initial relapse of subclinical disease.
Evidence Rating Level: 3 (Average)
Study Rundown: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a debilitating autoimmune disease of the central nervous system. Patients may present with a variety of symptoms that resemble those of other disorders, and thus biomedical imaging is routinely used to assist with detection of the disease. Despite increased sensitivity with modern scanning techniques, it is often difficult to definitively diagnosis and initiate treatment for MS patients given the inherent variability of the disease. Though the exact cause of MS is not fully understood, the disease is known to be intimately associated with abnormalities in the immune system, and most modern treatments act at least in part through modulation of immune cell function. Found in active inflammatory MS lesions, myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a proinflammatory enzyme abundantly secreted by inflammatory cells such as active neutrophils and macrophages. MPO activity is highly associated with demyelination, a process of damage to nerve cell myelin that is the hallmark of MS lesions. The goal of the present study was to determine if MPO-Gd, a gadolinium-based MR imaging contrast agent specific for MPO activity, is more sensitive than diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA)-Gd for revealing early subclinical and chronic disease activity in the brain. Using a well-studied mouse model of MS, the results showed MPO-Gd imaging was superior to MR imaging with DTPA-Gd for detection of subclinical disease activity in the murine brain during both acute and relapsing stages. While these findings represent a major step forward for MS diagnostics, further humans studies are warranted to definitively support the use of MPO-Gd imaging in MS patients.
Click to read the study in Radiology
Relevant Reading: Demyelinating diseases: myeloperoxidase as an imaging biomarker and therapeutic target.
In-Depth [animal study]: Researchers used the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) murine model of MS to compare MPO-Gd and DTPA-Gd MR imaging contrast agents for the detection of subclinical disease activity. Sixty-one female SJL mice were induced with EAE and imaged at 4.7 Tesla. Animal subjects were randomized to one of the two contrast agents, and all images were reviewed by two radiologists blinded to contrast agent and clinical disease severity. Measured parameters included total lesion volume, mean lesion volume, and total lesion number. The mice underwent MPO-Gd or DTPA-Gd MR imaging at multiple time points before development of clinical symptoms, during chronic disease at remission, and the first relapse. Following imaging, brain tissue from the mice was harvested for flow cytometry evaluation of immune cell subtypes and immunohistochemistry to confirm presence of disease. Using serial imaging, the researchers showed that MPO-Gd imaging was superior to MR imaging with DTPA-Gd for the detection of disease activity in the brain. Specifically, MPO-Gd imaging helped detect subtle disease activity 5 days prior to symptom onset (5.2 days before symptom onset, P=0.004), while DTPA-Gd imaging agents were only able to detect disease activity in the brain 2.3 days prior to symptom onset. MPO-Gd imaging detected more subclinical inflammatory lesions (3.1 vs 0.3, P=0.008) compared with DTPA-Gd, including in cases in which there was no evidence of overt blood-brain barrier breakdown or demyelination by conventional MR imaging. Results further showed that the number of MPO-Gd–enhancing brain lesions correlated with early infiltration of MPO-secreting inflammatory cells (r = 0.91), specifically monocytes and neutrophils.
More from this author: Patients report persistent quality-of-life impairments following ruptured brain aneurysms, Shear-wave elastography may improve prostate cancer detection, 7 tesla breast MRI may improve assessment of suspicious masses, VEGFR-targeted ultrasound may improve detection of pancreatic cancer, Cryoablation safe and effective for pain control in sternal metastases
Image: CC Roadnottaken Wikimedia Commons
©2014 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![Engineered stem cells mitigate liver damage caused by radiation [PreClinical]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Human_embryonic_stem_cells-75x75.png)

