Entecavir more effective than lamivudine in preventing HBV reactivation
1. Entecavir showed a significant reduction in the incidence of hepatitis B virus reactivation compared to lamivudine when used as prophylaxis during R-CHOP therapy1 for diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
2. There was no significant difference between entecavir and lamivudine with regards to frequency and severity of adverse events.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: Chemotherapy agents are known for weakening the immune system and increasing the risk of reactivating certain latent infections. Specifically, 26%-53% of patients undergoing chemotherapy are known to have reactivation of their latent hepatitis B virus (HBV). The standard of care is to use lamivudine to prevent HBV reactivation, but the number of lamivudine-resistant strains is rising, and entecavir has been proven to be more effective for treatment of HBV. This paper looked at patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (a type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma) and latent HBV who were treated with R-CHOP, a combination of potent immunosuppressive chemotherapy agents1, to see whether entecavir had the same or higher reduction in incidence of HBV reactivation.
This is the first randomized study that compared entecavir to lamivudine as prophylaxis during R-CHOP therapy in this patient population. Although it was a non-blinded study, observer bias was minimal since patients were randomized to their respective antiviral regimen and HBV reactivation was measured objectively. Although the sample size could have been larger, the study was sufficiently powered to provide results with sample sizes greater than 48 patients. In summary, this was a well-done randomized study that showed that entecavir was more effective in preventing HBV reactivation than lamivudine in patients receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy.
Click to read the study, published today in JAMA
Click to read an accompanying editorial, published today in JAMA
Relevant Reading: A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.
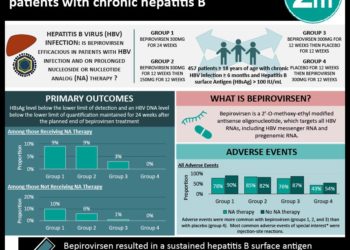
In-Depth [randomized controlled study]: This is a sub-study of a multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase III study that looked at both two different R-CHOP time regimens as well as the HBV reactivation incidence between those receiving lamivudine vs. entecavir. One-hundred and twenty one patients were randomized to receive either lamivudine or entecavir with equal number of patients in each chemotherapy arm. Patients required an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 3 or less, greater than 3 month life expectancy, latent HBV infection, and no prior history of antiviral therapy. Patients with concurrent hepatitis A,C,D, or E or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) were excluded. Results showed that the entecavir group had a much lower incidence of HBV reactivation while on chemotherapy than the lamivudine group (8.2% vs. 23.3%, respectively, 95%CI 2.4 to 27.8%; p=0.02). The entecavir group also had a significantly lower frequency of HBV-related hepatitis (p=0.003) as well as lower rate of chemotherapy disruption (p=0.002). There was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the two groups (24.6% in the entecavir group vs. 30% in the lamivudine group, 95%CI -10.5 to 21.3%; p=0.50).
1 R-CHOP consists of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone
More from this author: The CLARITY trial: Adding clopidogrel to STEMI management [Classics Series], Aspirin vs warfarin in atherosclerotic intracranial stenosis [Classics Series], The ARISTOTLE trial: Apixaban vs warfarin in atrial fibrillation [Classics Series],The TRITON trial: Prasugrel vs clopidogrel in ACS [Classics Series], Vena caval filters in pulmonary embolism prophylaxis [Classics Series]
Image: PD
©2014 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors, editors, staff or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.



![Engineered stem cells mitigate liver damage caused by radiation [PreClinical]](https://www.2minutemedicine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Human_embryonic_stem_cells-75x75.png)