Novel vaccine cocktail treats Staphylococcus aureus infections in mice (PreClinical)
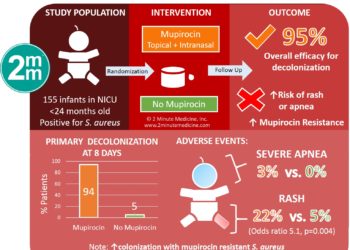
1. Mice treated with a vaccine cocktail containing five S. aureus antigens (4C-Staph) had significantly fewer adverse outcomes following S. aureus infection as compared to vaccines containing individual antigens.
2. Addition of a small molecule immune potentiator to 4C-Staph further significantly increased viability in mice treated with lethal doses of S. aureus.
Evidence Rating Level: 1 (Excellent)
Study Rundown: S. aureus infection can lead to dermatitis, kidney infections, pneumonia, and even death. Effective treatment for S. aureus infection remains elusive, in part due to the bacterium’s exceptional ability to combat multiple immunity pathways. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) remains a particularly critical global health threat.
In this study, researchers from the Novartis pharmaceutical company combined five antigens that play differing roles in the bacteria pathogenesis to create 4C-Staph, a vaccine designed to combat S. aureus infection on multiple levels. Most or all of the five antigens were shown to be present in each the six S. aureus strains they studied, which included four MRSA strains. Mice immunized with 4C-Staph and later injected with a sublethal dose of a S. aureus strain had fewer bacteria in their kidneys than mice immunized with any of the single vaccine components. The 4C-Staph vaccine also resulted in better outcomes than immunization with IsdB, which has been shown to effectively treat S. aureus in earlier studies. Related survival results were found in multiple models of infection; for example when mice were treated intraperitoneally with a lethal S. aureus dose, 4C-Staph immunization significantly increased survival rates over controls. Finally, the researchers added a novel small molecule designed to provoke the immune response to 4C-Staph, forming 4CT7-Staph. Mice immunized with 4CT7-Staph and then given lethal intraperitoneal doses of various S. aureus strains exhibited survival rates above 75%, even better than mice immunized with 4C-Staph alone.
This work presents a promising potential vaccine against S. aureus, which has thus far eluded treatment in many cases. Going forward, a comprehensive assessment of adverse outcomes of 4C-Staph immunization is needed before human studies can commence.
Click to read the study in PNAS
Relevant Reading: Challenges for a universal Staphylococcus aureus vaccine
In-Depth [animal study]: The antigens included in 4C-Staph were ferric hydroxamate uptake D2 and conserved staphylococcal antigen 1A, which are both S. aureus surface proteins, and α-hemolysin, ess extracellular A and ess extracellular B, which are all secreted by the bacterium. Western blotting confirmed that all or most of the vaccine components were present in the six strains of S. aureus studied.
In the renal abscess model used in this study, immunized mice were infected intravenously with sublethal injections of S. aureus at 10 days following a second immunization and sacrificed four days later. For five strains studied, 4C-Staph most significantly decreased the bacterial levels in kidney homogenates from these mice (p=0.003 to p<0.0001, n=16-20 per group) when compared with unloaded aluminum hydroxide vaccine (alum). 4C-Staph was also more effective than individual vaccine components or IsdB in reducing bacteria load (not always significant). The peritonitis model, in which mice were intraperitoneally infected with lethal S. aureus doses, followed the same timeline as the renal abscess model. Survival curves for mice separately infected with each of the six strains showed that 4C-Staph vaccination resulted in 53-78% survival at 15 days, which was significantly higher than those given alum (p=0.001 to p<0.0001) or IsdB, when tested (p=0.012 to p<0.0001, n=32-88 per group).
The small molecule adjuvant added to 4C-Staph specifically targets Toll-like receptor 7. The resulting 4CT7-Staph formulation significantly increased titer levels of most of the antigens in the vaccine as compared to the 4C-Staph formulation. 4CT7-Staph immunized mice also survived longer than 4C-Staph vaccinated mice when separately infected with multiple S. aureus strains in the peritonitis model (p=0.041 to p=0.0059, n=32-64 per group).
Image: PD
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.