Quick Take: Small Bowel Healing Detected by Endoscopy in Patients With Crohn’s Disease After Treatment With Antibodies Against Tumor Necrosis Factor
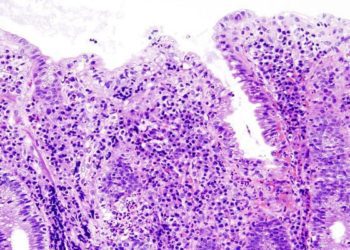
In patients with Crohn’s disease (CD), endoscopic evidence of healing after treatment is associated with favorable outcomes. Anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents have been shown to induce ileocolonic healing in CD, however the impact of these agents on gross small bowel healing as indicated by endoscopy has not been studied. In this case series, 116 patients with ileal or ileocolonic CD treated with anti-TNF agents at a single center in Japan were evaluated using balloon-assisted enteroscopy (BAE) to assess endoscopic healing (EH) in the small bowel and colon before and after anti-TNF therapy. Secondary outcomes included the rate of complete ulcer healing and endoscopic response (defined as a reduction in the Simple Endoscopy Score for CD by 50% or more). At baseline, 40% of patients had only ileal involvement, and 60% of patients had ileocolonic involvement; 75% of patients were male, and 63% of patients were anti-TNF naïve. In total, 46 patients received infliximab and 70 patients received adalimumab. Researchers found that 35% of patients achieved small bowel EH and 79% of patients achieved colonic EH during anti-TNF maintenance therapy; the rate of small bowel EH was significantly lower than that of colonic EH (p<0.001). Failure to achieve small bowel EH was found to be significantly associated with stricturing or penetrating disease (p=0.014), lack of concomitant treatment with immunomodulators (p=0.015), and having received previous treatment with an anti-TNF agent (p=0.018). Prognostically, small bowel EH was associated with better disease outcomes than non-small bowel EH (relapse, p<0.001; hospitalization, p=0.001; surgery, p=0.035). In summary, this study indicates that small bowel Crohn’s disease is less likely to demonstrate endoscopic healing after anti-TNF therapy than colonic Crohn’s disease. The findings of this study also indicate that patients that achieve small bowel healing have a more favorable prognosis compared to those that achieve non-small bowel healing.
Click to read the study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Image: PD
©2019 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.