Rate of occult fracture evaluations for child abuse insufficient
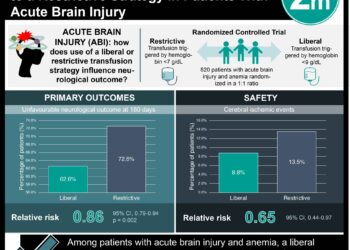
1. Less than half of children (48%) under age 2 who presented to a hospital with concern for physical abuse or non-accidental injury had underwent an evaluation for occult fractures.
2. Only half of infants under age 1 who presented with concern for a non-motor vehicle crash-related traumatic brain injury (TBI) and femur fractures underwent occult fracture evaluations.
Evidence Rating Level: 2 (Good)
Study Rundown: In children with suspected physical abuse, also known as non-accidental trauma, a skeletal survey (SS) to identify occult fractures is the gold standard in evaluating injuries and confirming abuse. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) has recommended SSs in all cases of suspected physical abuse in children younger than age 2 years. However, previous research has suggested that SSs are not routinely performed in those who may require them, with evaluation rates varying across hospitals in the United States. Authors of the current study sought to examine the rate of occult fracture examination in U.S. hospitals and quantify variations. They studied physically abused children <2 years old as well as infants <1 year old who had TBI and femur fractures. Results indicated that only 48% of children under age 2 who presented to a hospital with concern for non-accidental trauma were found to have undergone an evaluation for occult fractures. Similarly, only 51% and 53% of infants under age 1 who presented with concern for a non-motor vehicle crash-related TBI and femur fractures, respectively, underwent occult fracture evaluations. Limitations included reliance on administrative data, which may have coding errors, and unobserved patient-level factors, such as self-report of trauma. Nonetheless, these findings have implications for physicians encountering children who may be victims of non-accidental trauma. Adherence to AAP guidelines recommending SSs is required in order to detect abuse and prevent further harm to this vulnerable group of children.
Click to read the study, published today, in Pediatrics
Relevant Reading: Use of the skeletal survey in the evaluation of child maltreatment
In-Depth [retrospective cohort]: Study participants included 4486 children who were treated at 366 U.S. hospitals from 2009 to 2013; the sample was taken from the Premier database. Children included those <2 years old (n = 2502) with a diagnosis of physical abuse as well as infants <1 year old (n = 2433) with non-motor vehicle crash-related TBI (65%) or femur fractures (35%). Results indicated that evaluations for occult fractures were performed in 48% of the 2502 children with an abuse diagnosis, in 51% of the 1574 infants with traumatic brain injury, and in 53% of the 859 infants with femur fractures. Results indicated significant variation in occult fracture evaluation rates, ranging from 15% to 100% (p < 0.001). Forty-eight percent of children diagnosed with physical abuse received occult fracture evaluation. Among these children, odds of evaluation varied by race, with black children having the lowest odds of evaluation. The odds of evaluation were also higher at teaching vs. non-teaching hospitals. There were also regional differences, with southern United States having the highest odds of evaluation. Government-sponsored insurance increased the odds of evaluation for infants with both TBI and femur fractures. Evaluation rates ranged from 26% to 98% for the infant TBI group and 26% to 77% for the femur fracture group.
Image: CC
©2015 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. All rights reserved. No works may be reproduced without expressed written consent from 2 Minute Medicine, Inc. Inquire about licensing here. No article should be construed as medical advice and is not intended as such by the authors or by 2 Minute Medicine, Inc.